Page 221 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 221
Chapter 5. Surface treatments ofjibers and effects on composite properties 203
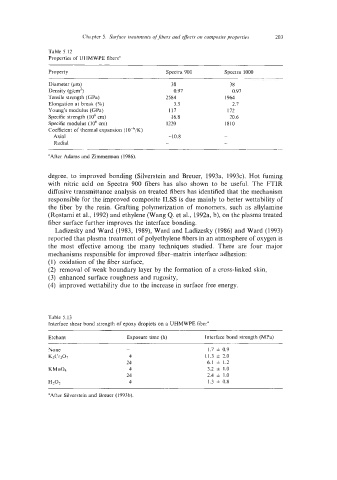
Table 5.12
Properties of UHMWPE fibers"
______
~
Property Spectra 900 Spectra 1000
Diameter (pm) 38 38
Density wan3) 0.97 0.97
Tensile strength (GPa) 2584 1964
Elongation at break (?'in) 3.5 2.7
Young's modulus (GPa) 117 172
Specific strength (IO6 an) 16.8 20.6
Specific modulus (lo6 cm) 1220 1810
Coefficient of thermal expansion (10-6/K)
Axial -10.8
Radial -
"After Adams and Zimmerman (1986).
degree, to improved bonding (Silverstein and Breuer, 1993a, 1993~). Hot fuming
with nitric acid on Spectra 900 fibers has also shown to be useful. The FTIR
diffusive transmittance analysis on treated fibers has identified that the mechanism
responsible for the improved composite ILSS is due mainly to better wettability of
the fiber by the resin. Grafting polymerization of monomers, such as allylamine
(Rostami et al., 1992) and ethylene (Wang Q. et al., 1992a, b), on the plasma treated
fiber surface further improves the interface bonding.
Ladizesky and Ward (1983, 1989), Ward and Ladizesky (1986) and Ward (1993)
reported that plasma treatment of polyethylene fibers in an atmosphere of oxygen is
the most effective among the many techniques studied. There are four major
mechanisms responsible for improved fiber-matrix interface adhesion:
(1) oxidation of the fiber surface,
(2) removal of weak boundary layer by the formation of a cross-linked skin,
(3) enhanced surface roughness and rugosity,
(4) improved wettability due to the increase in surface free energy.
Table 5.13
Interface shear bond strength of epoxy droplets on a UHMWPE fiber"
Etchant Exposure time (h) Interface bond strength (MPd)
None - 1.7 * 0.9
K2CrZ07 4 11.3 & 2.0
24 6.1 f 1.2
KMn04 4 3.2 f 1.0
24 2.4 f 1.0
4 1.3 ?C 0.8
"After Silverstein and Breuer (1993b).