Page 223 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 223
Chapter 5. Surface treatments of fibers and effects on composite properties 205
Encouraged by the remarkable improvements in interface adhesion, many
researchers have employed plasma treatment techniques, notably Netravali and
coworkers (Li et al., 1992; Li and Netravali, 1992; Hild and Schwartz, 1992a, b). An
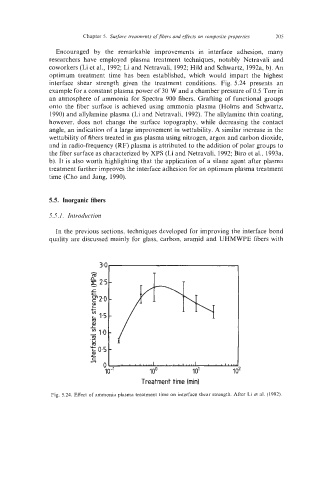
optimum treatment time has been established, which would impart the highest
interface shear strength given the treatment conditions. Fig. 5.24 presents an
example for a constant plasma power of 30 W and a chamber pressure of 0.5 Torr in
an atmosphere of ammonia for Spectra 900 fibers. Grafting of functional groups
onto the fiber surface is achieved using ammonia plasma (Holms and Schwartz,
1990) and allylamine plasma (Li and Netravali, 1992). The allylamine thin coating,
however, does not change the surface topography, while decreasing the contact
angle, an indication of a large improvement in wettability. A similar increase in the
wettability of fibers treated in gas plasma using nitrogen, argon and carbon dioxide,
and in radio-frequency (RF) plasma is attributed to the addition of polar groups to
the fiber surface as characterized by XPS (Li and Netravali, 1992; Biro et al., 1993a,
b). It is also worth highlighting that the application of a silane agent after plasma
treatment further improves the interface adhesion for an optimum plasma treatment
time (Cho and Jang, 1990).
5.5. Inorganic fibers
5.5.1. Introduction
In the previous sections, techniques developed for improving the interface bond
quality are discussed mainly for glass, carbon, aramid and UHMWPE fibers with
2
Treatment time (rnin)
Fig. 5.24. Effect of ammonia plasma treatment time on interface shear strength. After Li et al. (1992).