Page 26 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 26
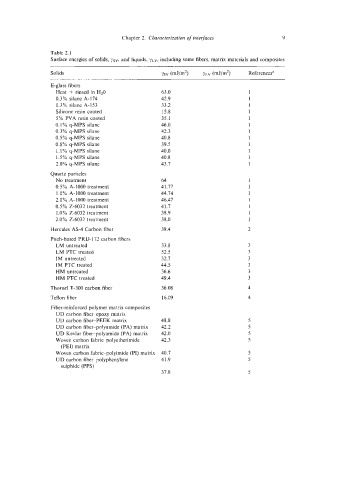
Chapter 2. Characterization of interfaces 9
Table 2.1
Surface energies of solids, ysv, and liquids, y~v, including some fibers, matrix materials and composites
Solids YSV (mJ/m2) YLV (mJlm’) Referencesa
E-glass fibers
Heat + rinsed in H20 63.0 1
0.3% silane A-174 42.9 i
0.3% silane A-153 33.2 1
Silicone resin coated 15.8 1
5% PVA resin coated 35.1 1
0.1% q-MPS silane 46.0 1
0.3% q-MPS silane 42.3 1
0.5% q-MPS silane 40.8 1
0.8% q-MPS silane 39.5 1
1.1 % q-MPS silane 40.0 1
1.5% q-MPS silane 40.8 1
2.0% q-MPS silane 43.7 1
Quartz particles
No treatment 64 1
0.5% A-IO00 treatment 41.77 1
1.0% A-1000 treatment 44.74 1
2.0% A-1000 treatment 46.41 1
0.5% 2-6032 treatment 41.7 1
1.0% 2-6032 treatment 38.9 1
2.0% 2-6032 treatment 38.0 1
Hercules AS-4 Carbon fiber 39.4 2
Pitch-based PRD-172 carbon fibers
LM untreated 33.8 3
LM PTC treated 52.5 3
IM untreated 32.7 3
IM FTC treated 44.5 3
HM untreated 36.6 3
HM PTC treated 49.4 3
Thornel T-300 carbon fiber 36.08 4
Teflon fiber 16.09 4
Fiber-reinforced polymer matrix composites
UD carbon fiber-epoxy matrix
UD carbon fiber-PEEK matrix 48.8 5
UD carbon fiber-polyamide (PA) matrix 42.2 5
UD Kevlar fiber-polyamide (PA) matrix 42.0 5
Woven carbon fabric-polyetherimide 42.3 5
(PEI) matrix
Woven carbon fabric-polyimide (PI) matrix 40.7 5
UD carbon fiber-polypbenylene 41.9 5
sulphide (PPS)
37.8 5