Page 29 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 29
12 Engineered interfaces in fiber reinforced composites
2.2.2. In terdiflision
A bond between two surfaces may be formed by the interdiffusion of atoms or
molecules across the interface. A fundamental feature of the interdiffusion
mechanism is that there must exist a thermodynamic equilibrium between the two
constituents. The bond strength in polymer matrix composites will depend on the
amount of molecular entanglement, the number of molecules involved and the
strength of the bonding between the molecules. Interdiffusion may be promoted by
the presence of solvents and the amount of diffusion will depend on the molecular
conformation, the constituents involved, and the ease of molecular motion. For
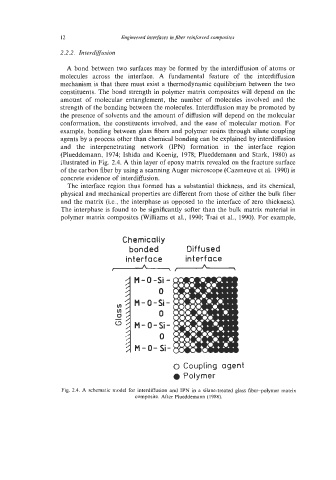
example, bonding between glass fibers and polymer resins through silane coupling
agents by a process other than chemical bonding can be explained by interdiffusion
and the interpenetrating network (IPN) formation in the interface region
(Plueddemann, 1974; Ishida and Koenig, 1978; Plueddemann and Stark, 1980) as
illustrated in Fig. 2.4. A thin layer of epoxy matrix revealed on the fracture surface
of the carbon fiber by using a scanning Auger microscope (Cazeneuve et al. 1990) is
concrete evidence of interdiffusion.
The interface region thus formed has a substantial thickness, and its chemical,
physical and mechanical properties are different from those of either the bulk fiber
and the matrix (i.e., the interphase as opposed to the interface of zero thickness).
The interphase is found to be significantly softer than the bulk matrix material in
polymer matrix composites (Williams et al., 1990; Tsai et al., 1990). For example,
Chemically
bonded Diffused
interface interface
+-7-
o Coupling agent
Polymer
Fig. 2.4. A schematic model for interdiffusion and IPN in a silane-treated glass fiber-polymer matrix
composite. After Plueddemann (1988).