Page 217 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 217
188 CHAPTER 4/LOGIC FUNCTION REPRESENTATION AND MINIMIZATION
\ CD C \ CD
1 1\
AB\ 00 01 I 11 lo"" 00 01 11 10
00 00 fo F 1 1
0
_ 1 3 2
01 01 0 F IE E)
4 5 7 6 R
11 1J 11 0 F E E
13 15 14 12 13 (15"~1 14 —
10 10 0 E + F fo ~o )
11 1C/ ^ 8- J 9 11 10 /
I /Wpos
D D
(a) (b)
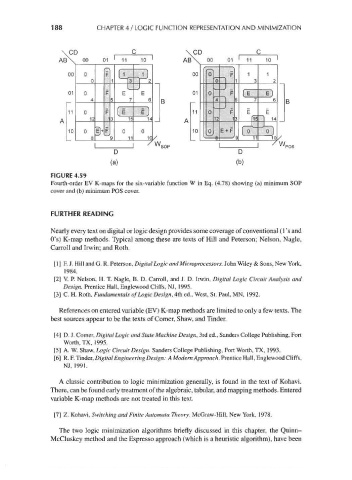
FIGURE 4.59
Fourth-order EV K-maps for the six-variable function W in Eq. (4.78) showing (a) minimum SOP
cover and (b) minimum POS cover.
FURTHER READING
Nearly every text on digital or logic design provides some coverage of conventional (1 's and
O's) K-map methods. Typical among these are texts of Hill and Peterson; Nelson, Nagle,
Carroll and Irwin; and Roth.
[1] F. J. Hill and G. R. Peterson, Digital Logic and Microprocessors. John Wiley & Sons, New York,
1984.
[2] V. P. Nelson, H. T. Nagle, B. D. Carroll, and J. D. Irwin, Digital Logic Circuit Analysis and
Design. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1995.
[3] C. H. Roth, Fundamentals of Logic Design, 4th ed., West, St. Paul, MN, 1992.
References on entered variable (EV) K-map methods are limited to only a few texts. The
best sources appear to be the texts of Comer, Shaw, and Tinder.
[4] D. J. Comer, Digital Logic and State Machine Design, 3rd ed., Sanders College Publishing, Fort
Worth, TX, 1995.
[5] A. W. Shaw, Logic Circuit Design. Sanders College Publishing, Fort Worth, TX, 1993.
[6] R. F. Tinder, Digital Engineering Design: A Modern Approach. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs,
NJ, 1991.
A classic contribution to logic minimization generally, is found in the text of Kohavi.
There, can be found early treatment of the algebraic, tabular, and mapping methods. Entered
variable K-map methods are not treated in this text.
[7] Z. Kohavi, Switching and Finite Automata Theory. McGraw-Hill, New York, 1978.
The two logic minimization algorithms briefly discussed in this chapter, the Quinn-
McCluskey method and the Espresso approach (which is a heuristic algorithm), have been