Page 214 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 214
4.12 WORKED EV K-MAP EXAMPLES 185
VCD C \ CD
AB \ 00 01 ' 11 10 ' J\ 00 01 11 10
,4
00 00 0) E 0 (0
0 1 2
)
01 01 E fi~ 0 1
v — J 4 5 ~t — > 7 6 R
11 11 1 1 E E
A 15 -44 12 13 — 1 15 ] 14
10 10 1 [ 0 0 T 0
1^ 8 9l I 11 lie/
I I / T SOP I ' POS
T
D D
(a) (b)
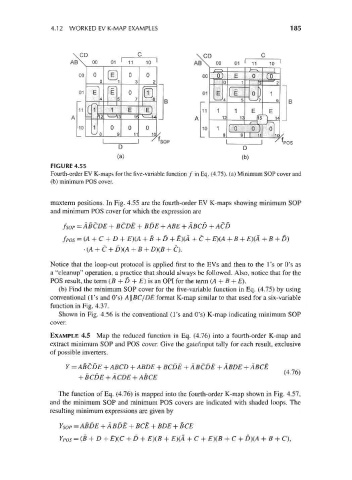
FIGURE 4.55
Fourth-order EV K-maps for the five-variable function / in Eq. (4.75). (a) Minimum SOP cover and
(b) minimum POS cover.
maxterm positions. In Fig. 4.55 are the fourth-order EV K-maps showing minimum SOP
and minimum POS cover for which the expression are
fsop = ABCDE + BCDE + BDE + ABE + ABCD + ACD
• (A + C + D)(A + B + D}(B + C).
Notice that the loop-out protocol is applied first to the EVs and then to the 1's or O's as
a "cleanup" operation, a practice that should always be followed. Also, notice that for the
POS result, the term (B + D + E) is an OPI for the term (A + B + E).
(b) Find the minimum SOP cover for the five-variable function in Eq. (4.75) by using
conventional (1's and O's) A\\BC/DE format K-map similar to that used for a six-variable
function in Fig. 4.37.
Shown in Fig. 4.56 is the conventional (1's and O's) K-map indicating minimum SOP
cover.
EXAMPLE 4.5 Map the reduced function in Eq. (4.76) into a fourth-order K-map and
extract minimum SOP and POS cover. Give the gate/input tally for each result, exclusive
of possible inverters.
Y = ABCDE + ABCD + ABDE + BCDE + ABCDE + ABDE + ABCE
- _ _ (4.76)
+ BCDE + A CDE + ABCE
The function of Eq. (4.76) is mapped into the fourth-order K-map shown in Fig. 4.57,
and the minimum SOP and minimum POS covers are indicated with shaded loops. The
resulting minimum expressions are given by
YSOP = ABDE + ABDE + BCE + BDE + BCE
Y POS = (B + D + E}(C +D + E)(B + E)(A + C + E}(B + C + D}(A + B + C),