Page 211 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 211
182 CHAPTER 4 / LOGIC FUNCTION REPRESENTATION AND MINIMIZATION
VBC
A\ oo 01 ' 11 10
1
1
•E
c c
(a) SOP Cover (b) POS Cover
FIGURE 4.50
(a) Minimum SOP cover and (b) minimum POS cover for the function /.
The compressed third-order K-maps representing SOP and POS cover are shown in
Fig. 4.50. Applying the loop-out protocol first to the EV and then to the 1's and O's gives
fsop = BCS +BS+ ABC + AC
B + S)(A + C + S)(B + C)
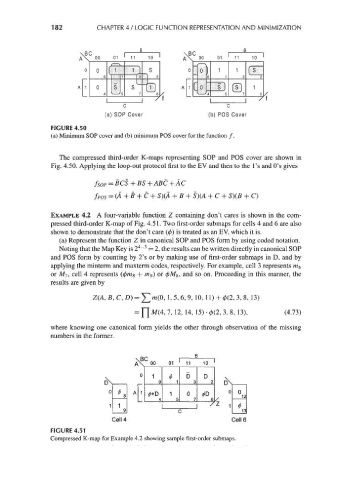
EXAMPLE 4.2 A four-variable function Z containing don't cares is shown in the com-
pressed third-order K-map of Fig. 4.51. Two first-order submaps for cells 4 and 6 are also
shown to demonstrate that the don't care (0) is treated as an EV, which it is.
(a) Represent the function Z in canonical SOP and POS form by using coded notation.
4 3
Noting that the Map Key is 2 ~ = 2, the results can be written directly in canonical SOP
and POS form by counting by 2's or by making use of first-order submaps in D, and by
applying the minterm and maxterm codes, respectively. For example, cell 3 represents m^
or M-j, cell 4 represents (0m 8 + mg) or 0Mg, and so on. Proceeding in this manner, the
results are given by
Z(A, B, C, D) = ^m(0, 1,5,6,9, 10, 11) + 0(2, 3, 8, 13)
= Y[ M(4, 7, 12, 14, 15) • 0(2, 3, 8, 13), (4.73)
where knowing one canonical form yields the other through observation of the missing
numbers in the former.
vBC
00 01 ' 11 10
1 0 1 D 3 D 2
f ^+D 4 * 1 5 0 7 *D 6
Cell 4 Cell 6
FIGURE 4.51
Compressed K-map for Example 4.2 showing sample first-order submaps.