Page 212 - Engineering Electromagnetics, 8th Edition
P. 212
194 ENGINEERING ELECTROMAGNETICS
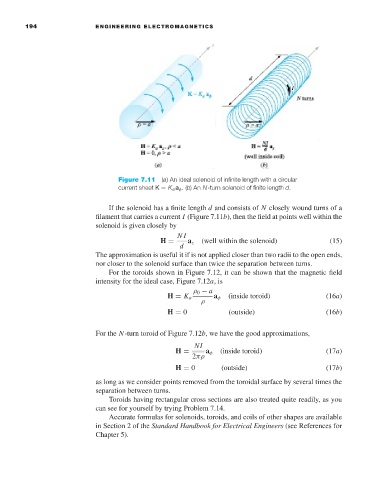
Figure 7.11 (a)An ideal solenoid of infinite length with a circular
current sheet K = K a a φ .(b)An N-turn solenoid of finite length d.
If the solenoid has a finite length d and consists of N closely wound turns of a
filament that carries a current I (Figure 7.11b), then the field at points well within the
solenoid is given closely by
NI
H = a z (well within the solenoid) (15)
d
The approximation is useful it if is not applied closer than two radii to the open ends,
nor closer to the solenoid surface than twice the separation between turns.
For the toroids shown in Figure 7.12, it can be shown that the magnetic field
intensity for the ideal case, Figure 7.12a,is
ρ 0 − a
H = K a a φ (inside toroid) (16a)
ρ
H = 0 (outside) (16b)
For the N-turn toroid of Figure 7.12b,wehave the good approximations,
NI
H = a φ (inside toroid) (17a)
2πρ
H = 0 (outside) (17b)
as long as we consider points removed from the toroidal surface by several times the
separation between turns.
Toroids having rectangular cross sections are also treated quite readily, as you
can see for yourself by trying Problem 7.14.
Accurate formulas for solenoids, toroids, and coils of other shapes are available
in Section 2 of the Standard Handbook for Electrical Engineers (see References for
Chapter 5).