Page 304 - Engineering Electromagnetics, 8th Edition
P. 304
286 ENGINEERING ELECTROMAGNETICS
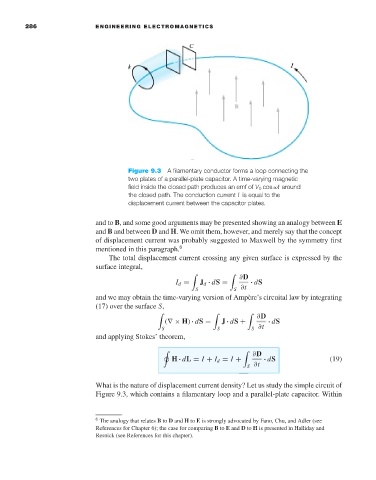
Figure 9.3 A filamentary conductor forms a loop connecting the
two plates of a parallel-plate capacitor. A time-varying magnetic
field inside the closed path produces an emf of V 0 cos ωt around
the closed path. The conduction current I is equal to the
displacement current between the capacitor plates.
and to B, and some good arguments may be presented showing an analogy between E
and B and between D and H.We omit them, however, and merely say that the concept
of displacement current was probably suggested to Maxwell by the symmetry first
mentioned in this paragraph. 6
The total displacement current crossing any given surface is expressed by the
surface integral,
∂D
I d = J d · dS = · dS
S S ∂t
and we may obtain the time-varying version of Amp`ere’s circuital law by integrating
(17) over the surface S,
∂D
(∇× H) · dS = J · dS + · dS
S S S ∂t
and applying Stokes’ theorem,
∂D
H · dL = I + I d = I + · dS (19)
S ∂t
What is the nature of displacement current density? Let us study the simple circuit of
Figure 9.3, which contains a filamentary loop and a parallel-plate capacitor. Within
6 The analogy that relates B to D and H to E is strongly advocated by Fano, Chu, and Adler (see
References for Chapter 6); the case for comparing B to E and D to H is presented in Halliday and
Resnick (see References for this chapter).