Page 142 - Engineering Plastics Handbook
P. 142
Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS) Resin 115
Extrusion ABS
The extrusion ABS resin is processed through a sheet or profile extrusion.
Although the resin in the form of a sheet may be used itself, depending on
the application, it is processed as the final product through thermoform-
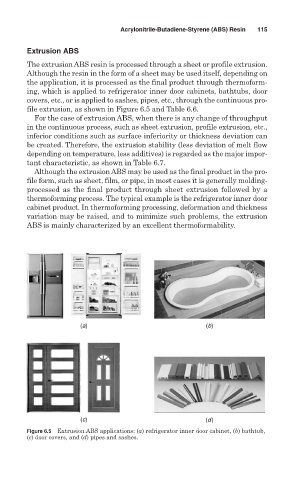
ing, which is applied to refrigerator inner door cabinets, bathtubs, door
covers, etc., or is applied to sashes, pipes, etc., through the continuous pro-
file extrusion, as shown in Figure 6.5 and Table 6.6.
For the case of extrusion ABS, when there is any change of throughput
in the continuous process, such as sheet extrusion, profile extrusion, etc.,
inferior conditions such as surface inferiority or thickness deviation can
be created. Therefore, the extrusion stability (less deviation of melt flow
depending on temperature, less additives) is regarded as the major impor-
tant characteristic, as shown in Table 6.7.
Although the extrusion ABS may be used as the final product in the pro-
file form, such as sheet, film, or pipe, in most cases it is generally molding-
processed as the final product through sheet extrusion followed by a
thermoforming process. The typical example is the refrigerator inner door
cabinet product. In thermoforming processing, deformation and thickness
variation may be raised, and to minimize such problems, the extrusion
ABS is mainly characterized by an excellent thermoformability.
(a) (b)
(c) (d)
Figure 6.5 Extrusion ABS applications: (a) refrigerator inner door cabinet, (b) bathtub,
(c) door covers, and (d) pipes and sashes.