Page 143 - Engineering Plastics Handbook
P. 143
116 Engineering Plastics
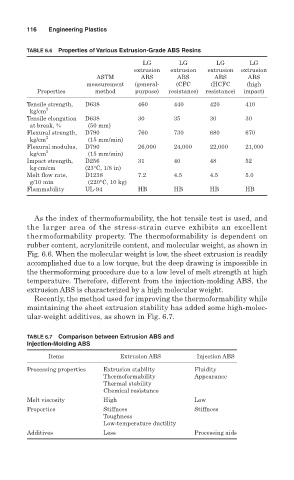
TABLE 6.6 Properties of Various Extrusion-Grade ABS Resins
LG LG LG LG
extrusion extrusion extrusion extrusion
ASTM ABS ABS ABS ABS
measurement (general- (CFC (HCFC (high
Properties method purpose) resistance) resistance) impact)
Tensile strength, D638 460 440 420 410
kg/cm 2
Tensile elongation D638 30 35 30 30
at break, % (50 mm)
Flexural strength, D790 760 730 680 670
kg/cm 2 (15 mm/min)
Flexural modulus, D790 26,000 24,000 22,000 21,000
kg/cm 2 (15 mm/min)
Impact strength, D256 31 40 48 52
kg⋅cm/cm (23°C, 1/8 in)
Melt flow rate, D1238 7.2 4.5 4.5 5.0
g/10 min (220°C, 10 kg)
Flammability UL-94 HB HB HB HB
As the index of thermoformability, the hot tensile test is used, and
the larger area of the stress-strain curve exhibits an excellent
thermoformability property. The thermoformability is dependent on
rubber content, acrylonitrile content, and molecular weight, as shown in
Fig. 6.6. When the molecular weight is low, the sheet extrusion is readily
accomplished due to a low torque, but the deep drawing is impossible in
the thermoforming procedure due to a low level of melt strength at high
temperature. Therefore, different from the injection-molding ABS, the
extrusion ABS is characterized by a high molecular weight.
Recently, the method used for improving the thermoformability while
maintaining the sheet extrusion stability has added some high-molec-
ular-weight additives, as shown in Fig. 6.7.
TABLE 6.7 Comparison between Extrusion ABS and
Injection-Molding ABS
Items Extrusion ABS Injection ABS
Processing properties Extrusion stability Fluidity
Thermoformability Appearance
Thermal stability
Chemical resistance
Melt viscosity High Low
Properties Stiffness Stiffness
Toughness
Low-temperature ductility
Additives Less Processing aids