Page 145 - Engineering Plastics Handbook
P. 145
118 Engineering Plastics
TABLE 6.8 Properties of Foaming Agents*
HFC-245fa R-11 HCFC-141b Cyclopentane
Molecular weight 134.0 137.4 116.9 70.0
Boiling point, °C 15.3 23.8 32.2 49.3
Specific gravity, g/cc at 20°C 1.32 1.49 1.24 0.74
Vapor pressure, kPa at 20°C 122 88.0 69.0 34.0
Vapor thermal conductivity, 0.012 0.008 0.010 0.011
kcal/mh°C at 44°C
Flame limit, vol% None None 7.6–17.7 1.4–9.4
Ignition point, °C None None None −37
Lift time in atmosphere, yr 8.4 50 9.4 A few days
GWP (R-11 = 1) 0.21 1.0 0.12 <0.001
*Utech 96 Paper 55, p. 355.
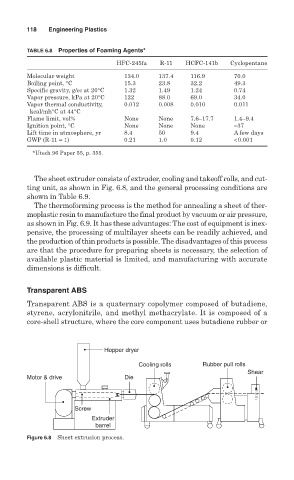
The sheet extruder consists of extruder, cooling and takeoff rolls, and cut-
ting unit, as shown in Fig. 6.8, and the general processing conditions are
shown in Table 6.9.
The thermoforming process is the method for annealing a sheet of ther-
moplastic resin to manufacture the final product by vacuum or air pressure,
as shown in Fig. 6.9. It has these advantages: The cost of equipment is inex-
pensive, the processing of multilayer sheets can be readily achieved, and
the production of thin products is possible. The disadvantages of this process
are that the procedure for preparing sheets is necessary, the selection of
available plastic material is limited, and manufacturing with accurate
dimensions is difficult.
Transparent ABS
Transparent ABS is a quaternary copolymer composed of butadiene,
styrene, acrylonitrile, and methyl methacrylate. It is composed of a
core-shell structure, where the core component uses butadiene rubber or
Hopper dryer
Cooling rolls Rubber pull rolls
Shear
Motor & drive Die
Screw
Extruder
barrel
Figure 6.8 Sheet extrusion process.