Page 172 - Engineering Plastics Handbook
P. 172
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) 145
0.2
Moisture content (%) 0.1 80°C
0.04
100°C
0.03
140°C 120°C
0 2 4 6 8
Hours
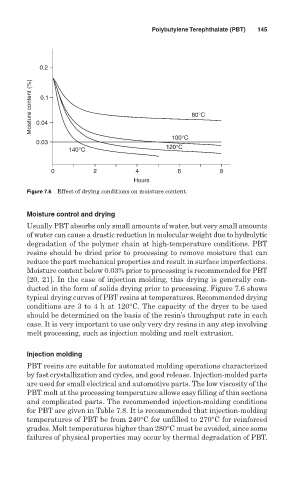
Figure 7.6 Effect of drying conditions on moisture content.
Moisture control and drying
Usually PBT absorbs only small amounts of water, but very small amounts
of water can cause a drastic reduction in molecular weight due to hydrolytic
degradation of the polymer chain at high-temperature conditions. PBT
resins should be dried prior to processing to remove moisture that can
reduce the part mechanical properties and result in surface imperfections.
Moisture content below 0.03% prior to processing is recommended for PBT
[20, 21]. In the case of injection molding, this drying is generally con-
ducted in the form of solids drying prior to processing. Figure 7.6 shows
typical drying curves of PBT resins at temperatures. Recommended drying
conditions are 3 to 4 h at 120°C. The capacity of the dryer to be used
should be determined on the basis of the resin’s throughput rate in each
case. It is very important to use only very dry resins in any step involving
melt processing, such as injection molding and melt extrusion.
Injection molding
PBT resins are suitable for automated molding operations characterized
by fast crystallization and cycles, and good release. Injection-molded parts
are used for small electrical and automotive parts. The low viscosity of the
PBT melt at the processing temperature allows easy filling of thin sections
and complicated parts. The recommended injection-molding conditions
for PBT are given in Table 7.8. It is recommended that injection-molding
temperatures of PBT be from 240°C for unfilled to 270°C for reinforced
grades. Melt temperatures higher than 280°C must be avoided, since some
failures of physical properties may occur by thermal degradation of PBT.