Page 174 - Engineering Plastics Handbook
P. 174
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) 147
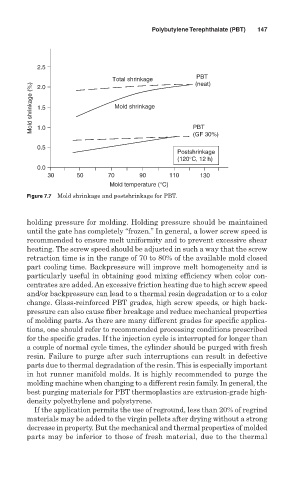
2.5
PBT
Total shrinkage (neat)
Mold shrinkage (%) 1.5 Mold shrinkage
2.0
1.0
PBT
(GF 30%)
0.5
Postshrinkage
(120°C, 12 h)
0.0
30 50 70 90 110 130
Mold temperature (°C)
Figure 7.7 Mold shrinkage and postshrinkage for PBT.
holding pressure for molding. Holding pressure should be maintained
until the gate has completely “frozen.” In general, a lower screw speed is
recommended to ensure melt uniformity and to prevent excessive shear
heating. The screw speed should be adjusted in such a way that the screw
retraction time is in the range of 70 to 80% of the available mold closed
part cooling time. Backpressure will improve melt homogeneity and is
particularly useful in obtaining good mixing efficiency when color con-
centrates are added. An excessive friction heating due to high screw speed
and/or backpressure can lead to a thermal resin degradation or to a color
change. Glass-reinforced PBT grades, high screw speeds, or high back-
pressure can also cause fiber breakage and reduce mechanical properties
of molding parts. As there are many different grades for specific applica-
tions, one should refer to recommended processing conditions prescribed
for the specific grades. If the injection cycle is interrupted for longer than
a couple of normal cycle times, the cylinder should be purged with fresh
resin. Failure to purge after such interruptions can result in defective
parts due to thermal degradation of the resin. This is especially important
in hot runner manifold molds. It is highly recommended to purge the
molding machine when changing to a different resin family. In general, the
best purging materials for PBT thermoplastics are extrusion-grade high-
density polyethylene and polystyrene.
If the application permits the use of reground, less than 20% of regrind
materials may be added to the virgin pellets after drying without a strong
decrease in property. But the mechanical and thermal properties of molded
parts may be inferior to those of fresh material, due to the thermal