Page 275 - Engineering Plastics Handbook
P. 275
Thermoplastic Polyimide (TPI) 237
200
Tensile strength, MPa 150
100
50
0
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350
(122) (212) (302) (392) (482) (572) (662)
Temperature, °C (°F)
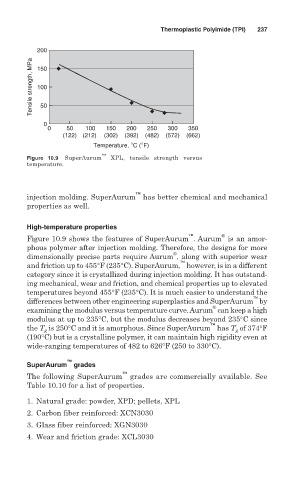
Figure 10.9 SuperAurum ™ XPL, tensile strength versus
temperature.
™
injection molding. SuperAurum has better chemical and mechanical
properties as well.
High-temperature properties
™ ®
Figure 10.9 shows the features of SuperAurum . Aurum is an amor-
phous polymer after injection molding. Therefore, the designs for more
®
dimensionally precise parts require Aurum , along with superior wear
™
and friction up to 455°F (235°C). SuperAurum, however, is in a different
category since it is crystallized during injection molding. It has outstand-
ing mechanical, wear and friction, and chemical properties up to elevated
temperatures beyond 455°F (235°C). It is much easier to understand the
™
differences between other engineering superplastics and SuperAurum by
®
examining the modulus versus temperature curve. Aurum can keep a high
modulus at up to 235°C, but the modulus decreases beyond 235°C since
™
the T is 250°C and it is amorphous. Since SuperAurum has T of 374°F
g
g
(190°C) but is a crystalline polymer, it can maintain high rigidity even at
wide-ranging temperatures of 482 to 626°F (250 to 330°C).
™
SuperAurum grades
™
The following SuperAurum grades are commercially available. See
Table 10.10 for a list of properties.
1. Natural grade: powder, XPD; pellets, XPL
2. Carbon fiber reinforced: XCN3030
3. Glass fiber reinforced: XGN3030
4. Wear and friction grade: XCL3030