Page 279 - Engineering Plastics Handbook
P. 279
Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) 241
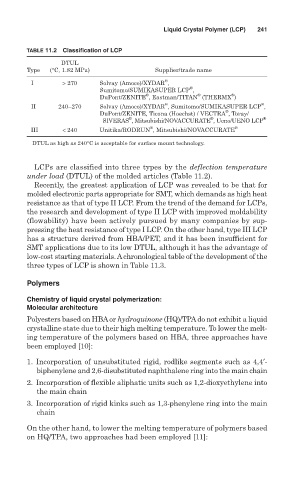
TABLE 11.2 Classification of LCP
DTUL
Type (°C, 1.82 MPa) Supplier/trade name
®
I > 270 Solvay (Amoco)/XYDAR ,
®
Sumitomo/SUMIKASUPER LCP ,
®
®
®
DuPont/ZENITE , Eastman/TITAN (THERMX )
®
®
II 240–270 Solvay (Amoco)/XYDAR , Sumitomo/SUMIKASUPER LCP ,
®
DuPont/ZENITE, Ticona (Hoechst) / VECTRA , Toray/
®
®
SIVERAS , Mitsubishi/NOVACCURATE , Ueno/UENO LCP ®
®
III < 240 Unitika/RODRUN , Mitsubishi/NOVACCURATE ®
DTUL as high as 240°C is acceptable for surface mount technology.
LCPs are classified into three types by the deflection temperature
under load (DTUL) of the molded articles (Table 11.2).
Recently, the greatest application of LCP was revealed to be that for
molded electronic parts appropriate for SMT, which demands as high heat
resistance as that of type II LCP. From the trend of the demand for LCPs,
the research and development of type II LCP with improved moldability
(flowability) have been actively pursued by many companies by sup-
pressing the heat resistance of type I LCP. On the other hand, type III LCP
has a structure derived from HBA/PET, and it has been insufficient for
SMT applications due to its low DTUL, although it has the advantage of
low-cost starting materials. Achronological table of the development of the
three types of LCP is shown in Table 11.3.
Polymers
Chemistry of liquid crystal polymerization:
Molecular architecture
Polyesters based on HBAor hydroquinone (HQ)/TPAdo not exhibit a liquid
crystalline state due to their high melting temperature. To lower the melt-
ing temperature of the polymers based on HBA, three approaches have
been employed [10]:
1. Incorporation of unsubstituted rigid, rodlike segments such as 4,4′-
biphenylene and 2,6-disubstituted naphthalene ring into the main chain
2. Incorporation of flexible aliphatic units such as 1,2-dioxyethylene into
the main chain
3. Incorporation of rigid kinks such as 1,3-phenylene ring into the main
chain
On the other hand, to lower the melting temperature of polymers based
on HQ/TPA, two approaches had been employed [11]: