Page 79 - Engineering Plastics Handbook
P. 79
Properties 53
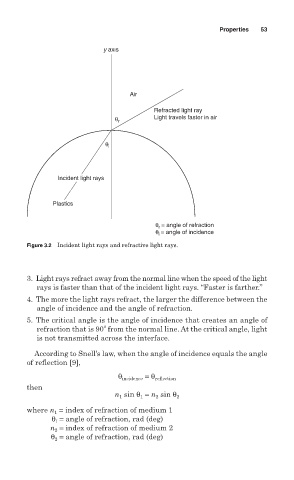
y axis
Air
Refracted light ray
θ r Light travels faster in air
θ i
Incident light rays
Plastics
θ = angle of refraction
r
θ = angle of incidence
i
Figure 3.2 Incident light rays and refractive light rays.
3. Light rays refract away from the normal line when the speed of the light
rays is faster than that of the incident light rays. “Faster is farther.”
4. The more the light rays refract, the larger the difference between the
angle of incidence and the angle of refraction.
5. The critical angle is the angle of incidence that creates an angle of
o
refraction that is 90 from the normal line. At the critical angle, light
is not transmitted across the interface.
According to Snell’s law, when the angle of incidence equals the angle
of reflection [9],
=θ
θ incidence reflection
then
1
n sin θ 1 = n 2 sin θ 2
where n 1 = index of refraction of medium 1
θ 1 = angle of refraction, rad (deg)
n 2 = index of refraction of medium 2
θ 2 = angle of refraction, rad (deg)