Page 181 - Enhanced Oil Recovery in Shale and Tight Reservoirs
P. 181
Water injection 165
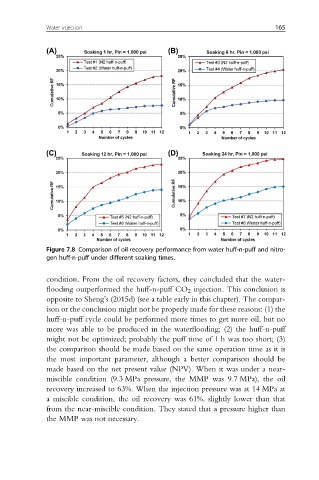
Figure 7.8 Comparison of oil recovery performance from water huff-n-puff and nitro-
gen huff-n-puff under different soaking times.
condition. From the oil recovery factors, they concluded that the water-
flooding outperformed the huff-n-puff CO 2 injection. This conclusion is
opposite to Sheng’s (2015d) (see a table early in this chapter). The compar-
ison or the conclusion might not be properly made for these reasons: (1) the
huff-n-puff cycle could be performed more times to get more oil, but no
more was able to be produced in the waterflooding; (2) the huff-n-puff
might not be optimized; probably the puff time of 1 h was too short; (3)
the comparison should be made based on the same operation time as it is
the most important parameter, although a better comparison should be
made based on the net present value (NPV). When it was under a near-
miscible condition (9.3 MPa pressure, the MMP was 9.7 MPa), the oil
recovery increased to 63%. When the injection pressure was at 14 MPa at
a miscible condition, the oil recovery was 61%, slightly lower than that
from the near-miscible condition. They stated that a pressure higher than
the MMP was not necessary.