Page 117 -
P. 117
Chapter 4 • Development Life Cycle 93
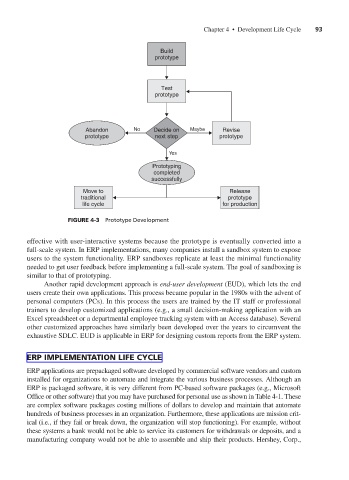
Build
prototype
Test
prototype
Abandon No Decide on Maybe Revise
prototype next step prototype
Yes
Prototyping
completed
successfully
Move to Release
traditional prototype
life cycle for production
FIGURE 4-3 Prototype Development
effective with user-interactive systems because the prototype is eventually converted into a
full-scale system. In ERP implementations, many companies install a sandbox system to expose
users to the system functionality. ERP sandboxes replicate at least the minimal functionality
needed to get user feedback before implementing a full-scale system. The goal of sandboxing is
similar to that of prototyping.
Another rapid development approach is end-user development (EUD), which lets the end
users create their own applications. This process became popular in the 1980s with the advent of
personal computers (PCs). In this process the users are trained by the IT staff or professional
trainers to develop customized applications (e.g., a small decision-making application with an
Excel spreadsheet or a departmental employee tracking system with an Access database). Several
other customized approaches have similarly been developed over the years to circumvent the
exhaustive SDLC. EUD is applicable in ERP for designing custom reports from the ERP system.
ERP IMPLEMENTATION LIFE CYCLE
ERP applications are prepackaged software developed by commercial software vendors and custom
installed for organizations to automate and integrate the various business processes. Although an
ERP is packaged software, it is very different from PC-based software packages (e.g., Microsoft
Office or other software) that you may have purchased for personal use as shown in Table 4-1. These
are complex software packages costing millions of dollars to develop and maintain that automate
hundreds of business processes in an organization. Furthermore, these applications are mission crit-
ical (i.e., if they fail or break down, the organization will stop functioning). For example, without
these systems a bank would not be able to service its customers for withdrawals or deposits, and a
manufacturing company would not be able to assemble and ship their products. Hershey, Corp.,