Page 119 -
P. 119
Chapter 4 • Development Life Cycle 95
2. Middle of the Road. A middle-of-the-road ERP implementation plan involves some changes
in the core ERP modules and a significant amount of BPR. The middle-of-the-road
approach is not as expensive as the comprehensive approach or as straightforward as the
vanilla approach.
3. Vanilla. A vanilla ERP implementation plan utilizes core ERP functionality and exploits
the best practice business processes built into the software. A company following a vanilla
implementation will have to simply align their business processes to the ERP system,
rather than modify the software. By eliminating or minimizing the required BPR, the
project’s costs and time required for the implementation are minimized.
ERP Implementation Methodology
Methodology refers to a systematic approach to solving a business problem. ERP methodology
builds on the theory that an enterprise can maximize its returns by maximizing the utiliza-
tion of its fixed supply of resources. Information technology, with its increasing computer
power and the ability to correlate pieces of information, has proven to be the best tool for
business problem solving. Like SDLC, an ERP development life cycle provides a systematic
approach to implementing ERP software in the changing but limited-resource organizational
environment.
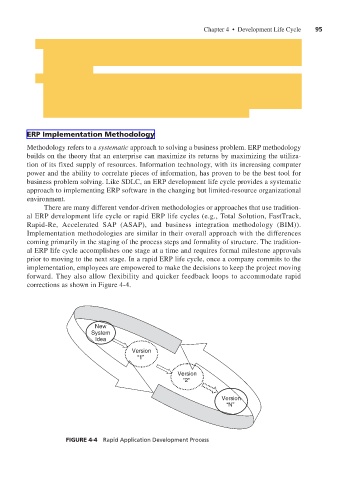
There are many different vendor-driven methodologies or approaches that use tradition-
al ERP development life cycle or rapid ERP life cycles (e.g., Total Solution, FastTrack,
Rapid-Re, Accelerated SAP (ASAP), and business integration methodology (BIM)).
Implementation methodologies are similar in their overall approach with the differences
coming primarily in the staging of the process steps and formality of structure. The tradition-
al ERP life cycle accomplishes one stage at a time and requires formal milestone approvals
prior to moving to the next stage. In a rapid ERP life cycle, once a company commits to the
implementation, employees are empowered to make the decisions to keep the project moving
forward. They also allow flexibility and quicker feedback loops to accommodate rapid
corrections as shown in Figure 4-4.
New
System
Idea
Version
“1”
Version
“2”
Version
“N”
FIGURE 4-4 Rapid Application Development Process