Page 297 -
P. 297
Chapter 9 • Organizational Change and Business Process Reengineering 255
GL Posting and
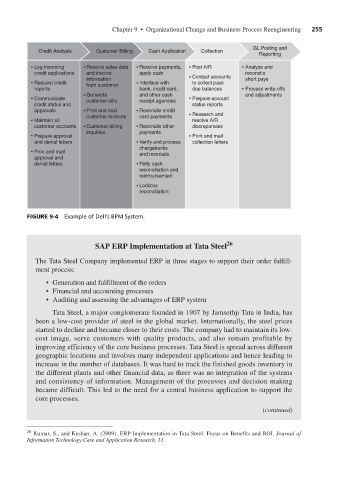
Credit Analysis Customer Billing Cash Application Collection
Reporting
Log incoming Receive sales data Receive payments, Post A/R Analyze and
credit applications and invoice apply cash reconcile
information Contact accounts short pays
Request credit from customer Interface with to collect past-
reports bank, credit card, due balances Process write-offs
Generate and other cash and adjustments
Communicate customer bills receipt agencies Prepare account
credit status and status reports
approvals Print and mail Reconcile credit
customer invoices card payments Research and
Maintain all resolve A/R
customer accounts Customer billing Reconcile other discrepancies
inquiries payments
Prepare approval Print and mail
and denial letters Verify and process collection letters
chargebacks
Print and mail and reversals
approval and
denial letters Petty cash
reconciliation and
reimbursement
Lockbox
reconciliation
FIGURE 9-4 Example of Dell’s BPM System.
SAP ERP Implementation at Tata Steel 26
The Tata Steel Company implemented ERP in three stages to support their order fulfill-
ment process:
•Generation and fulfillment of the orders
•Financial and accounting processes
•Auditing and assessing the advantages of ERP system
Tata Steel, a major conglomerate founded in 1907 by Jamsethji Tata in India, has
been a low-cost provider of steel in the global market. Internationally, the steel prices
started to decline and became closer to their costs. The company had to maintain its low-
cost image, serve customers with quality products, and also remain profitable by
improving efficiency of the core business processes. Tata Steel is spread across different
geographic locations and involves many independent applications and hence leading to
increase in the number of databases. It was hard to track the finished goods inventory in
the different plants and other financial data, as there was no integration of the systems
and consistency of information. Management of the processes and decision making
became difficult. This led to the need for a central business application to support the
core processes.
(Continued)
26 Kumar, S., and Keshan, A. (2009). ERP Implementation in Tata Steel: Focus on Benefits and ROI. Journal of
Information Technology Case and Application Research, 11.