Page 90 -
P. 90
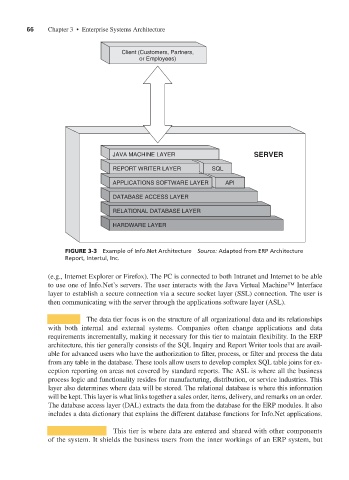
66 Chapter 3 • Enterprise Systems Architecture
Client (Customers, Partners,
or Employees)
JAVA MACHINE LAYER SERVER
REPORT WRITER LAYER SQL
APPLICATIONS SOFTWARE LAYER API
DATABASE ACCESS LAYER
RELATIONAL DATABASE LAYER
HARDWARE LAYER
FIGURE 3-3 Example of Info.Net Architecture Source: Adapted from ERP Architecture
Report, Intertul, Inc.
(e.g., Internet Explorer or Firefox). The PC is connected to both Intranet and Internet to be able
to use one of Info.Net’s servers. The user interacts with the Java Virtual Machine™ Interface
layer to establish a secure connection via a secure socket layer (SSL) connection. The user is
then communicating with the server through the applications software layer (ASL).
DATA TIER The data tier focus is on the structure of all organizational data and its relationships
with both internal and external systems. Companies often change applications and data
requirements incrementally, making it necessary for this tier to maintain flexibility. In the ERP
architecture, this tier generally consists of the SQL Inquiry and Report Writer tools that are avail-
able for advanced users who have the authorization to filter, process, or filter and process the data
from any table in the database. These tools allow users to develop complex SQL table joins for ex-
ception reporting on areas not covered by standard reports. The ASL is where all the business
process logic and functionality resides for manufacturing, distribution, or service industries. This
layer also determines where data will be stored. The relational database is where this information
will be kept. This layer is what links together a sales order, items, delivery, and remarks on an order.
The database access layer (DAL) extracts the data from the database for the ERP modules. It also
includes a data dictionary that explains the different database functions for Info.Net applications.
APPLICATION TIER This tier is where data are entered and shared with other components
of the system. It shields the business users from the inner workings of an ERP system, but