Page 112 - Environmental Control in Petroleum Engineering
P. 112
The Impact of Drilling and Production Operations 99
Na +
SAR = 2+
Mg
where the cation concentrations are expressed in millimoles/liter.
Concentrations are determined by direct chemical analysis of reserves
pit liquids or aqueous extracts of waste solids or soils. High sodium
levels (SAR greater than 12) in soil solutions cause Ca and Mg
deficiencies in plants (American Petroleum Institute, 1989b).
3.3.2 Impact on Aquatic Organisms
Most, but not all, produced waters have a salt content higher than
that found in the local ecosystems. The discharge of water having a
higher salt content can impact aquatic organisms. High concentrations
of sodium chloride can affect the development of embryos and fetuses
and can cause fetal death. High salt concentrations can also affect the
development of the musculoskeletal system and cause eye, skin, and
upper respiratory system irritation.
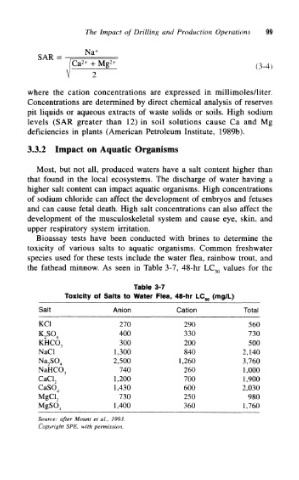
Bioassay tests have been conducted with brines to determine the
toxicity of various salts to aquatic organisms. Common freshwater
species used for these tests include the water flea, rainbow trout, and
the fathead minnow. As seen in Table 3-7, 48-hr LC 50 values for the
Table 3-7
Toxicity of Salts to Water Flea, 48-hr LC 50 (mg/L)
Salt Anion Cation Total
KC1 270 290 560
400 330 730
K 2S0 4
KHCO, 300 200 500
NaCl 1,300 840 2,140
2,500 1,260 3,760
Na 2S0 4
740 260 1,000
NaHCO 3
CaCI 2 1,200 700 1,900
1,430 600 2,030
CaSO 4
730 250
MgCl 7 980
1,400 360 1,760
MgSO 4
Source: after Mount et ai, 1993,
Copyright SPE, with permission.