Page 115 - Environmental Control in Petroleum Engineering
P. 115
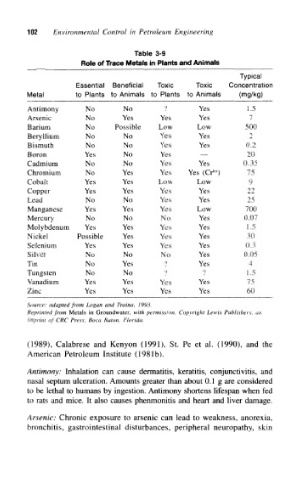
102 Environmental Control in Petroleum Engineering
Table 3-9
Role of Trace Metals in Plants and Animals
Typical
Essential Beneficial Toxic Toxic Concentration
Metal to Plants to Animals to Plants to Animals (mg/kg)
Antimony No No 9 Yes 1.5
Arsenic No Yes Yes Yes 7
Barium No Possible Low Low 500
Beryllium No No Yes Yes 2
Bismuth No No Yes Yes 0.2
Boron Yes No Yes _ 20
Cadmium No No Yes Yes 0.35
6+
Chromium No Yes Yes Yes (Cr ) 75
Cobalt Yes Yes Low Low 9
Copper Yes Yes Yes Yes 22
Lead No No Yes Yes 25
Manganese Yes Yes Yes Low 700
Mercury No No No Yes 0.07
Molybdenum Yes Yes Yes Yes 1.5
Nickel Possible Yes Yes Yes 30
Selenium Yes Yes Yes Yes 0.3
Silver No No No Yes 0.05
Tin No Yes '? Yes 4
Tungsten No No 9 ? 1.5
Vanadium Yes Yes Yes Yes 75
Zinc Yes Yes Yes Yes 60
Source: adapted from Logan and Traina, 1993.
Reprinted from Metals in Groundwater, with permission. Copyright Lewis Publishers, an
imprint of CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida.
(1989), Calabrese and Kenyon (1991), St. Pe et al. (1990), and the
American Petroleum Institute (1981b).
Antimony: Inhalation can cause dermatitis, keratitis, conjunctivitis, and
nasal septum ulceration. Amounts greater than about 0.1 g are considered
to be lethal to humans by ingestion. Antimony shortens lifespan when fed
to rats and mice. It also causes phenmonitis and heart and liver damage.
Arsenic: Chronic exposure to arsenic can lead to weakness, anorexia,
bronchitis, gastrointestinal disturbances, peripheral neuropathy, skin