Page 299 - Environmental Nanotechnology Applications and Impacts of Nanomaterials
P. 299
284 Principles and Methods
0
–20
Ψ/mV –40
–60
–80
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
pH
(a)
4
2
0
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
pH
(b)
1.0
Dg/Dw 0.8
0.6
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
pH
(c)
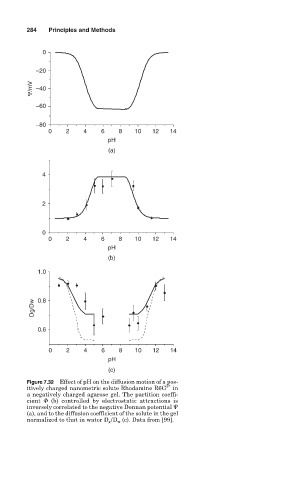
Figure 7.32 Effect of pH on the diffusion motion of a pos-
2+
itively charged nanometric solute Rhodamine R6G in
a negatively charged agarose gel. The partition coeffi-
cient
(b) controlled by electrostatic attractions is
inversely correlated to the negative Donnan potential
(a), and to the diffusion coefficient of the solute in the gel
normalized to that in water D g /D w (c). Data from [99].