Page 193 - Excel Data Analysis
P. 193
10 537547 Ch09.qxd 3/4/03 12:13 PM Page 179
AUTOMATING ACTIONS WITH MACROS 9
There are essentially two different types of functions:
private and public. All modules within the workbook
can access a public function. However, only other
procedures within the same module can access a private
function. You mark a function as private by placing
Private before the Function statement as in the
example Private Function SampleFunc(Param)
As Integer. Excel considers any functions that do not
have the Private keyword to be public. Therefore,
using the Public keyword is unnecessary because a
function with no keyword is the same as one with the
Public keyword.
Other functions and subroutines within the same
module typically call private functions. Because
functions return a value, they are typically called as part
of an expression. For example, you can assign the value
returned by a function to a variable: FunctionValue
= SampleFunc(Param). This line of code exists in a
subroutine that calls the function. When Excel
encounters this code, the function executes using the
value of the Param parameter, and the result of the
function is placed in the FunctionValue variable.
PERSONAL.xls!Find_Average
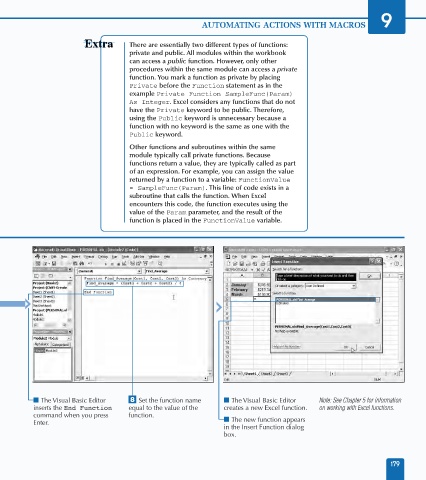
■ The Visual Basic Editor ° Set the function name ■ The Visual Basic Editor Note: See Chapter 5 for information
inserts the End Function equal to the value of the creates a new Excel function. on working with Excel functions.
command when you press function.
Enter. ■ The new function appears
in the Insert Function dialog
box.
179