Page 196 - Excel for Scientists and Engineers: Numerical Methods
P. 196
CHAPTER 8 ROOTS OF EOUATIONS 173
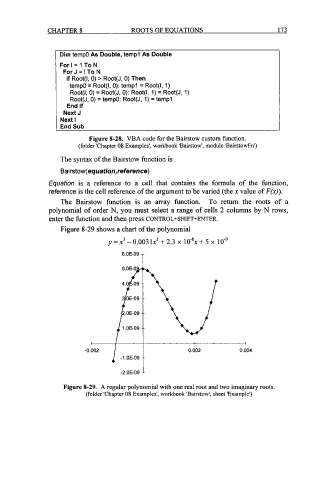
Dim tempo As Double, templ As Double
For I = 1 To N
For J = I To N
If Root(l, 0) > Root(J, 0) Then
tempo = Root(l, 0): temp1 = Root(l, 1)
Root(l, 0) = Root(J, 0): Root(l, 1) = Root(J, 1)
Root(J, 0) =tempo: Root(J, 1) = templ
End If
Next J
Next I
End Sub
Figure 8-28. VBA code for the Bairstow custom function.
(folder 'Chapter 08 Examples', workbook 'Bairstow', module 'BairstowFn')
The syntax of the Bairstow function is
Bairstow( equation, reference)
Equation is a reference to a cell that contains the formula of the function,
reference is the cell reference of the argument to be varied (the x value of F(x)).
The Bairstow function is an array function. To return the roots of a
polynomial of order N, you must select a range of cells 2 columns by N rows,
enter the function and then press CONTROL+SHIFT+ENTER.
Figure 8-29 shows a chart of the polynomial
y=x3-0.0031x2+2.3 x 10-*x+5 x lo-'
6.OE-09 T
A
5.OE-0
f:: //J f
-
1.OE-09 --
-0.002 0.002 0.004
-1 .OE-09
-2.OE-09 I
Figure 8-29. A regular polynomial with one real root and two imaginary roots.
(folder 'Chapter 08 Examples', workbook 'Bairstow', sheet 'Example')