Page 149 - Failure Analysis Case Studies II
P. 149
134
Secondary
associated with -
initiation
6 in. crack Secondary
initiation
associated with
,6 ft crack
Region in which
fracture face
was destroyed Similar region to that
by mechanical seen on starboard
damage, and fracture face. Crack is
where major thought to have
crack is thought arrested here during
to have arrested first incident
during first
incident
Primary initiation
(Fig. 20)
W
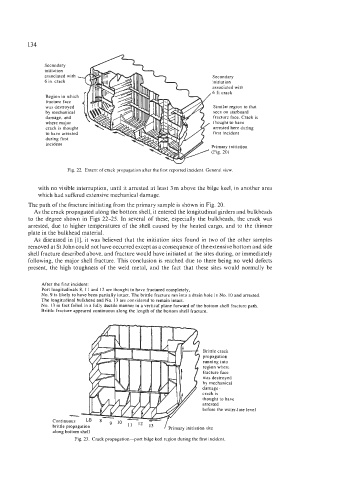
Fig. 22. Extent of crack propagation after the first reported incident. General view.
with no visible interruption, until it arrested at least 3 m above the bilge keel, in another area
which had suffered extensive mechanical damage.
The path of the fracture initiating from the primary sample is shown in Fig. 20.
As the crack propagated along the bottom shell, it entered the longitudinal girders and bulkheads
to the degree shown in Figs 22-25. In several of these, especially the bulkheads, the crack was
arrested, due to higher temperatures of the shell caused by the heated cargo, and to the thinner
plate in the bulkhead material.
As discussed in [l], it was believed that the initiation sites found in two of the other samples
removed at St John could not have occurred except as a consequence of the extensive bottom and side
shell fracture described above, and fracture would have initiated at the sites during, or immediately
following, the major shell fracture. This conclusion is reached due to there being no weld defects
present, the high toughness of the weld metal, and the fact that these sites would normally be
After the first incident:
Port longitudinals 8, I1 and 12 are thought to have fractured completely,
No. 9 is likely to have been partially intact. The brittle fracture ran into a drain hole in No. IO and arrested.
The longitudinal bulkhead and No. 13 are considered to remain intact.
No. 13 in fact failed in a fully ductile manner in a vertical plane forward of the bottom shell fracture path.
Brittle fracture appeared continuous along the length of the bottom shell fracture.
level
Fig. 23. Crack propagation-port bilge keel region during the first incident.