Page 140 - Fair, Geyer, and Okun's Water and wastewater engineering : water supply and wastewater removal
P. 140
JWCL344_ch03_061-117.qxd 8/17/10 7:48 PM Page 102
102 Chapter 3 Water Sources: Groundwater
art that has evolved along a number of more or less regional lines. In the United States, well
drillers are generally given much latitude in the choice of a suitable method. What they un-
dertake to do is to sink a well of specified size at a fixed price per foot. Ordinarily, therefore,
the engineer gives his attention not so much to drilling operations as to the adequacy, suit-
ability, and economics of proposed developments and the location of the works.
Well categories generally take their names from the methods by which wells are con-
structed. Shallow wells can be dug, driven, jetted, or bored.
3.17.1 Dug Wells
Small dug wells are generally excavated by hand. In loose overburden, they are cribbed with
timber; lined with brick, rubble, or concrete; or cased with large-diameter vitrified tile or con-
crete pipe. In rock, they are commonly left unlined. Excavation is continued until water flows
in more rapidly than it can be bailed out. Dug wells should be completed when the water table
is at or near its lowest level. Otherwise, they may have to be deepened at a later date.
Large and deep dug wells are often constructed by sinking their liners as excavation pro-
ceeds. The lead ring has a steel cutting edge; new rings are added as excavation progresses.
3.17.2 Driven and Jetted Wells
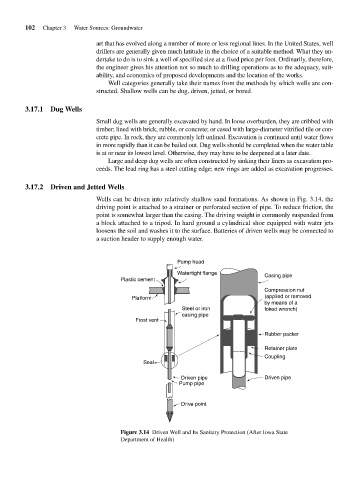
Wells can be driven into relatively shallow sand formations. As shown in Fig. 3.14, the
driving point is attached to a strainer or perforated section of pipe. To reduce friction, the
point is somewhat larger than the casing. The driving weight is commonly suspended from
a block attached to a tripod. In hard ground a cylindrical shoe equipped with water jets
loosens the soil and washes it to the surface. Batteries of driven wells may be connected to
a suction header to supply enough water.
Pump head
Watertight flange Casing pipe
Plastic cement
Compression nut
Platform (applied or removed
by means of a
Steel or iron foked wrench)
casing pipe
Frost vent
Rubber packer
Retainer plate
Coupling
Seal
Driven pipe Driven pipe
Pump pipe
Drive point
Figure 3.14 Driven Well and Its Sanitary Protection (After Iowa State
Department of Health)