Page 208 - Fair, Geyer, and Okun's Water and wastewater engineering : water supply and wastewater removal
P. 208
JWCL344_ch05_154-193.qxd 8/2/10 9:44 PM Page 170
170 Chapter 5 Water Hydraulics, Transmission, and Appurtenances
EXAMPLE 5.5 CIRCULAR CONDUIT EQUIVALENCE TO A HORSESHOE CONDUIT
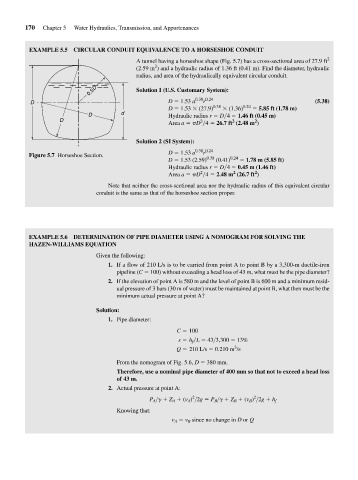
A tunnel having a horseshoe shape (Fig. 5.7) has a cross-sectional area of 27.9 ft 2
2
(2.59 m ) and a hydraulic radius of 1.36 ft (0.41 m). Find the diameter, hydraulic
radius, and area of the hydraulically equivalent circular conduit.
0.5D Solution 1 (U.S. Customary System):
r
D D 1.53 a 0.38 0.24 (5.38)
D 1.53 (27.9) 0.38 (1.36) 0.24 5.85 ft (1.78 m)
D d Hydraulic radius r D 4 1.46 ft (0.45 m)
D 2 2 2
Area a D 4 26.7 ft (2.48 m )
Solution 2 (SI System):
D 1.53 a 0.38 0.24
r
Figure 5.7 Horseshoe Section. 0.38 0.24
D 1.53 (2.59) (0.41) 1.78 m (5.85 ft)
Hydraulic radius r D 4 0.45 m (1.46 ft)
2
2
2
Area a D 4 2.48 m (26.7 ft )
Note that neither the cross-sectional area nor the hydraulic radius of this equivalent circular
conduit is the same as that of the horseshoe section proper.
EXAMPLE 5.6 DETERMINATION OF PIPE DIAMETER USING A NOMOGRAM FOR SOLVING THE
HAZEN-WILLIAMS EQUATION
Given the following:
1. If a flow of 210 L/s is to be carried from point A to point B by a 3,300-m ductile-iron
pipeline (C 100) without exceeding a head loss of 43 m, what must be the pipe diameter?
2. If the elevation of point A is 580 m and the level of point B is 600 m and a minimum resid-
ual pressure of 3 bars (30 m of water) must be maintained at point B, what then must be the
minimum actual pressure at point A?
Solution:
1. Pipe diameter:
C 100
s h f L 43>3,300 13%
3
Q 210 L/s 0.210 m /s
From the nomogram of Fig. 5.6, D 380 mm.
Therefore, use a nominal pipe diameter of 400 mm so that not to exceed a head loss
of 43 m.
2. Actual pressure at point A:
2 2
P A > Z A (v A ) >2g P B > Z B (v B ) >2g h f
Knowing that:
v A v B since no change in D or Q