Page 314 - Fiber Bragg Gratings
P. 314
6.8 Side-tap and long-period grating band-pass filters 291
the transmission loss spectrum of an LPG, in Fig. 6.46b. Both gratings
were written in the same fiber.
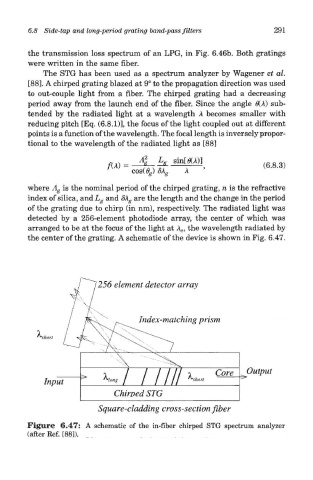
The STG has been used as a spectrum analyzer by Wagener et al.
[88]. A chirped grating blazed at 9° to the propagation direction was used
to out-couple light from a fiber. The chirped grating had a decreasing
period away from the launch end of the fiber. Since the angle 0(X) sub-
tended by the radiated light at a wavelength A becomes smaller with
reducing pitch [Eq. (6.8.1)], the focus of the light coupled out at different
points is a function of the wavelength. The focal length is inversely propor-
tional to the wavelength of the radiated light as [88]
where A g is the nominal period of the chirped grating, n is the refractive
index of silica, and L g and SA g are the length and the change in the period
of the grating due to chirp (in nm), respectively. The radiated light was
detected by a 256-element photodiode array, the center of which was
arranged to be at the focus of the light at A c, the wavelength radiated by
the center of the grating. A schematic of the device is shown in Fig. 6.47.
Figure 6.47: A schematic of the in-fiber chirped STG spectrum analyzer
(after Ref. [88]).