Page 392 - Fiber Bragg Gratings
P. 392
8.2 Static and dynamic properties of FGLs 369
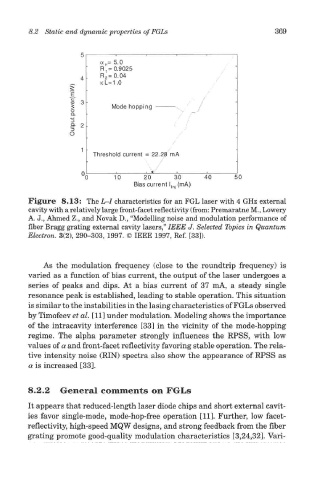
Figure 8.13: The L-I characteristics for an FGL laser with 4 GHz external
cavity with a relatively large front-facet reflectivity (from: Premaratne M., Lowery
A. J., Ahmed Z., and Novak D., "Modelling noise and modulation performance of
fiber Bragg grating external cavity lasers," IEEE J. Selected Topics in Quantum
Electron. 3(2), 290-303, 1997. © IEEE 1997, Ref. [33]).
As the modulation frequency (close to the roundtrip frequency) is
varied as a function of bias current, the output of the laser undergoes a
series of peaks and dips. At a bias current of 37 mA, a steady single
resonance peak is established, leading to stable operation. This situation
is similar to the instabilities in the lasing characteristics of FGLs observed
by Timofeev et al. [11] under modulation. Modeling shows the importance
of the intracavity interference [33] in the vicinity of the mode-hopping
regime. The alpha parameter strongly influences the RPSS, with low
values of a and front-facet reflectivity favoring stable operation. The rela-
tive intensity noise (RIN) spectra also show the appearance of RPSS as
a is increased [33].
8.2.2 General comments on FGLs
It appears that reduced-length laser diode chips and short external cavit-
ies favor single-mode, mode-hop-free operation [11]. Further, low facet-
reflectivity, high-speed MQW designs, and strong feedback from the fiber
grating promote good-quality modulation characteristics [3,24,32]. Vari-