Page 96 - Fiber Fracture
P. 96
FRACTURE PROCESSES IN FINE SILICON CARBIDE FIBRES 81
Fig. 4. The micro-structure of the Hi-Nicalon fibre is composed of Sic grains of 5 nm average size and free
carbon.
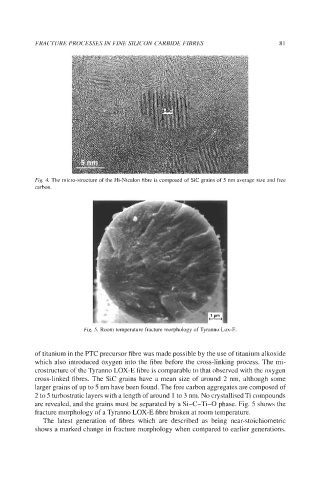
Fig. 5. Room temperature fracture morphology of Tyranno Lox-E
of titanium in the PTC precursor fibre was made possible by the use of titanium alkoxide
which also introduced oxygen into the fibre before the cross-linking process. The mi-
crostructure of the Tyranno LOX-E fibre is comparable to that observed with the oxygen
cross-linked fibres. The Sic grains have a mean size of around 2 nm, although some
larger grains of up to 5 nm have been found. The free carbon aggregates are composed of
2 to 5 turbostratic layers with a length of around 1 to 3 nm. No crystallised Ti compounds
are revealed, and the grains must be separated by a Si-C-Ti-0 phase. Fig. 5 shows the
fracture morphology of a Tyranno LOX-E fibre broken at room temperature.
The latest generation of fibres which are described as being near-stoichiometric
shows a marked change in fracture morphology when compared to earlier generations.