Page 98 - Fiber Fracture
P. 98
FRACTURE PROCESSES IN FINE SILICON CARBIDE FIBRES 83
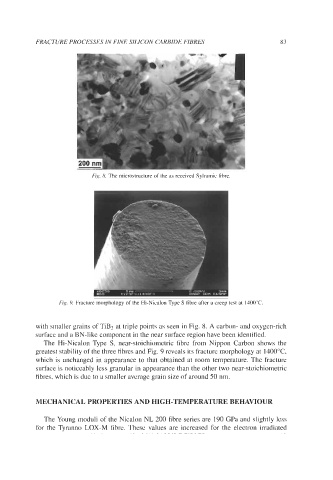
Fig. 8. Thc microstructure of the as received Sylramic fibre
Fig. 9. Fracture morphology of the Hi-Nicalon Type S fibre after a creep test at 1400°C.
with smaller grains of TiB2 at triple points as seen in Fig. 8. A carbon- and oxygen-rich
surface and a BN-like component in the near surface region have been identified.
The Hi-Nicalon Type S, near-stoichiometric fibre from Nippon Carbon shows the
greatest stability of the three fibres and Fig. 9 reveals its fracture morphology at 14OO0C,
which is unchanged in appearance to that obtained at room temperature. The fracture
surface is noticeably less granular in appearance than the other two near-stoichiometric
fibres, which is due to a smaller average grain size of around 50 nm.
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES AND HIGH-TEMPERATURE BEHAVIOUR
The Young moduli of the Nicalon NL 200 fibre series are 190 GPa and slightly less
for the Tyranno LOX-M fibre. These values are increased for the electron irradiated