Page 219 - Finance for Non-Financial Managers
P. 219
Siciliano12.qxd 2/8/2003 7:35 AM Page 200
Finance for Non-Financial Managers
200
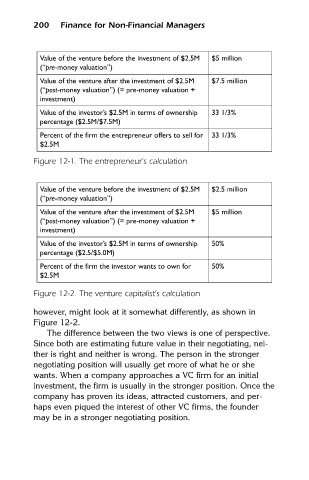
Value of the venture before the investment of $2.5M
(“pre-money valuation”)
Value of the venture after the investment of $2.5M $5 million
$7.5 million
(“post-money valuation”) (= pre-money valuation +
investment)
Value of the investor’s $2.5M in terms of ownership 33 1/3%
percentage ($2.5M/$7.5M)
Percent of the firm the entrepreneur offers to sell for 33 1/3%
$2.5M
Figure 12-1. The entrepreneur’s calculation
Value of the venture before the investment of $2.5M $2.5 million
(“pre-money valuation”)
Value of the venture after the investment of $2.5M $5 million
(“post-money valuation”) (= pre-money valuation +
investment)
Value of the investor’s $2.5M in terms of ownership 50%
percentage ($2.5/$5.0M)
Percent of the firm the investor wants to own for 50%
$2.5M
Figure 12-2. The venture capitalist’s calculation
however, might look at it somewhat differently, as shown in
Figure 12-2.
The difference between the two views is one of perspective.
Since both are estimating future value in their negotiating, nei-
ther is right and neither is wrong. The person in the stronger
negotiating position will usually get more of what he or she
wants. When a company approaches a VC firm for an initial
investment, the firm is usually in the stronger position. Once the
company has proven its ideas, attracted customers, and per-
haps even piqued the interest of other VC firms, the founder
may be in a stronger negotiating position.