Page 244 - Finite Element Analysis with ANSYS Workbench
P. 244
12.2 Finite Volume Method 235
U
dA ( I x F n y )E n dS = 0
I
A t S
where n and n are directions cosines of the unit vector normal to
x
y
the cell edge.
The integrand in the second integral term represents the
flux F normal to the cell edge,
n
F = E I n F I n
y
x
n
So that the finite volume equations reduce to,
U dA = F dS
n
A t S
The fluxes normal to the cell edge for the four Navier-Stokes
equations are,
u n x v n y V n
2 p u n uv n uV np
F
= x y = n x
n
n x uv 2 p v n y vV n np y
u n pu v pv n
x y V n pV n
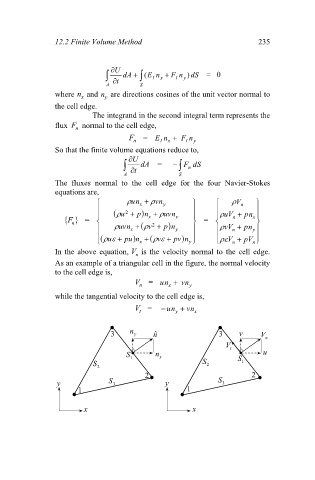
In the above equation, V is the velocity normal to the cell edge.
n
As an example of a triangular cell in the figure, the normal velocity
to the cell edge is,
V = nu n v y
x
n
while the tangential velocity to the cell edge is,
V = u n n v x
y
t
3 n y n ˆ 3 v V n
V t
S 1 n x S u
S 2 S 2 1
2 2
y S 3 y S 3
1 1
x x