Page 198 - Finite Element Modeling and Simulations with ANSYS Workbench
P. 198
Modeling and Solution Techniques 183
5.10 Review of Learning Objectives
Now that you have finished this chapter you should be able to
1. Apply symmetry in meshing and analysis for a symmetrical structure.
2. Apply axisymmetric model and elements when the structure and loads are
axisymmetric.
3. Select proper equation solvers (direct or iterative) for the FE model at hand.
4. Understand the sources of errors in FEA and the error indicators.
5. Know how to refine a mesh using h-refinement or p-refinement.
6. Apply the various techniques in the FEA of a model using ANSYS Workbench.
PROBLEMS
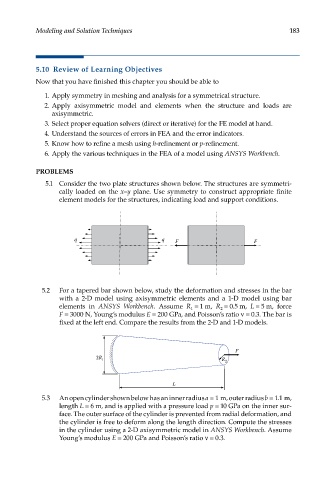
5.1 Consider the two plate structures shown below. The structures are symmetri-
cally loaded on the x–y plane. Use symmetry to construct appropriate finite
element models for the structures, indicating load and support conditions.
q q F F
5.2 For a tapered bar shown below, study the deformation and stresses in the bar
with a 2-D model using axisymmetric elements and a 1-D model using bar
elements in ANSYS Workbench. Assume R = 1 m, R = 0.5 m, L = 5 m, force
2
1
F = 3000 N, Young’s modulus E = 200 GPa, and Poisson’s ratio ν = 0.3. The bar is
fixed at the left end. Compare the results from the 2-D and 1-D models.
F
2R 1 R 2
L
5.3 An open cylinder shown below has an inner radius a = 1 m, outer radius b = 1.1 m,
length L = 6 m, and is applied with a pressure load p = 10 GPa on the inner sur-
face. The outer surface of the cylinder is prevented from radial deformation, and
the cylinder is free to deform along the length direction. Compute the stresses
in the cylinder using a 2-D axisymmetric model in ANSYS Workbench. Assume
Young’s modulus E = 200 GPa and Poisson’s ratio ν = 0.3.