Page 199 - Finite Element Modeling and Simulations with ANSYS Workbench
P. 199
184 Finite Element Modeling and Simulation with ANSYS Workbench
a
b L
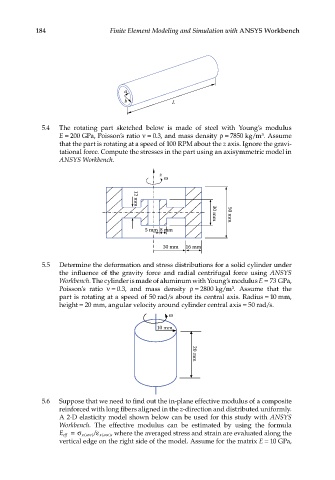
5.4 The rotating part sketched below is made of steel with Young’s modulus
E = 200 GPa, Poisson’s ratio ν = 0.3, and mass density ρ = 7850 kg/m . Assume
3
that the part is rotating at a speed of 100 RPM about the z axis. Ignore the gravi-
tational force. Compute the stresses in the part using an axisymmetric model in
ANSYS Workbench.
z
12 mm
5 mm 8 mm 30 mm 50 mm
30 mm 16 mm
5.5 Determine the deformation and stress distributions for a solid cylinder under
the influence of the gravity force and radial centrifugal force using ANSYS
Workbench. The cylinder is made of aluminum with Young’s modulus E = 73 GPa,
Poisson’s ratio ν = 0.3, and mass density ρ = 2800 kg/m . Assume that the
3
part is rotating at a speed of 50 rad/s about its central axis. Radius = 10 mm,
height = 20 mm, angular velocity around cylinder central axis = 50 rad/s.
10 mm 20 mm
5.6 Suppose that we need to find out the in-plane effective modulus of a composite
reinforced with long fibers aligned in the z-direction and distributed uniformly.
A 2-D elasticity model shown below can be used for this study with ANSYS
Workbench. The effective modulus can be estimated by using the formula
x ave ε/ x ave), where the averaged stress and strain are evaluated along the
E eff =σ ( ) (
vertical edge on the right side of the model. Assume for the matrix E = 10 GPa,