Page 112 - Flexible Robotics in Medicine
P. 112
Flexible steerable manipulator utilizing complementary configuration 97
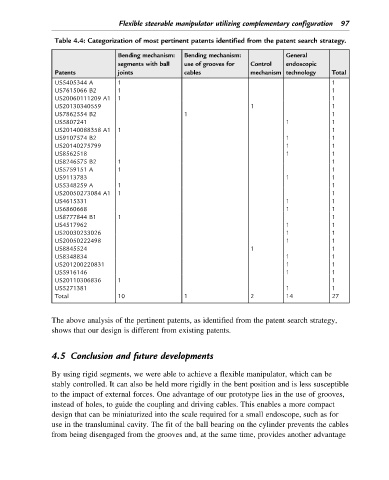
Table 4.4: Categorization of most pertinent patents identified from the patent search strategy.
Bending mechanism: Bending mechanism: General
segments with ball use of grooves for Control endoscopic
Patents joints cables mechanism technology Total
US5405344 A 1 1
US7615066 B2 1 1
US20060111209 A1 1 1
US20130340559 1 1
US7862554 B2 1 1
US5807241 1 1
US20140088358 A1 1 1
US9107574 B2 1 1
US20140275799 1 1
US8562518 1 1
US8246575 B2 1 1
US5759151 A 1 1
US9113783 1 1
US5348259 A 1 1
US20050273084 A1 1 1
US4615331 1 1
US6860668 1 1
US8777844 B1 1 1
US4517962 1 1
US20030233026 1 1
US20050222498 1 1
US8845524 1 1
US8348834 1 1
US201200220831 1 1
US5916146 1 1
US20110306836 1 1
US5271381 1 1
Total 10 1 2 14 27
The above analysis of the pertinent patents, as identified from the patent search strategy,
shows that our design is different from existing patents.
4.5 Conclusion and future developments
By using rigid segments, we were able to achieve a flexible manipulator, which can be
stably controlled. It can also be held more rigidly in the bent position and is less susceptible
to the impact of external forces. One advantage of our prototype lies in the use of grooves,
instead of holes, to guide the coupling and driving cables. This enables a more compact
design that can be miniaturized into the scale required for a small endoscope, such as for
use in the transluminal cavity. The fit of the ball bearing on the cylinder prevents the cables
from being disengaged from the grooves and, at the same time, provides another advantage