Page 158 - Flexible Robotics in Medicine
P. 158
144 Chapter 5
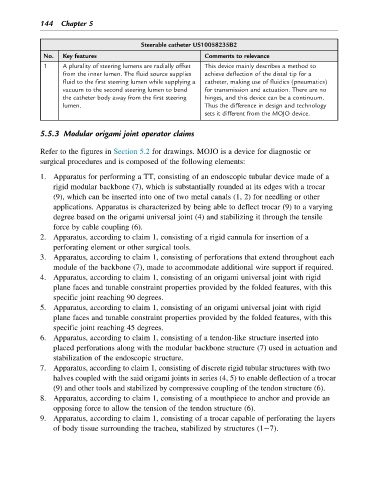
Steerable catheter US10058235B2
No. Key features Comments to relevance
1 A plurality of steering lumens are radially offset This device mainly describes a method to
from the inner lumen. The fluid source supplies achieve deflection of the distal tip for a
fluid to the first steering lumen while supplying a catheter, making use of fluidics (pneumatics)
vacuum to the second steering lumen to bend for transmission and actuation. There are no
the catheter body away from the first steering hinges, and this device can be a continuum.
lumen. Thus the difference in design and technology
sets it different from the MOJO device.
5.5.3 Modular origami joint operator claims
Refer to the figures in Section 5.2 for drawings. MOJO is a device for diagnostic or
surgical procedures and is composed of the following elements:
1. Apparatus for performing a TT, consisting of an endoscopic tubular device made of a
rigid modular backbone (7), which is substantially rounded at its edges with a trocar
(9), which can be inserted into one of two metal canals (1, 2) for needling or other
applications. Apparatus is characterized by being able to deflect trocar (9) to a varying
degree based on the origami universal joint (4) and stabilizing it through the tensile
force by cable coupling (6).
2. Apparatus, according to claim 1, consisting of a rigid cannula for insertion of a
perforating element or other surgical tools.
3. Apparatus, according to claim 1, consisting of perforations that extend throughout each
module of the backbone (7), made to accommodate additional wire support if required.
4. Apparatus, according to claim 1, consisting of an origami universal joint with rigid
plane faces and tunable constraint properties provided by the folded features, with this
specific joint reaching 90 degrees.
5. Apparatus, according to claim 1, consisting of an origami universal joint with rigid
plane faces and tunable constraint properties provided by the folded features, with this
specific joint reaching 45 degrees.
6. Apparatus, according to claim 1, consisting of a tendon-like structure inserted into
placed perforations along with the modular backbone structure (7) used in actuation and
stabilization of the endoscopic structure.
7. Apparatus, according to claim 1, consisting of discrete rigid tubular structures with two
halves coupled with the said origami joints in series (4, 5) to enable deflection of a trocar
(9) and other tools and stabilized by compressive coupling of the tendon structure (6).
8. Apparatus, according to claim 1, consisting of a mouthpiece to anchor and provide an
opposing force to allow the tension of the tendon structure (6).
9. Apparatus, according to claim 1, consisting of a trocar capable of perforating the layers
of body tissue surrounding the trachea, stabilized by structures (1 7).