Page 154 - Flexible Robotics in Medicine
P. 154
140 Chapter 5
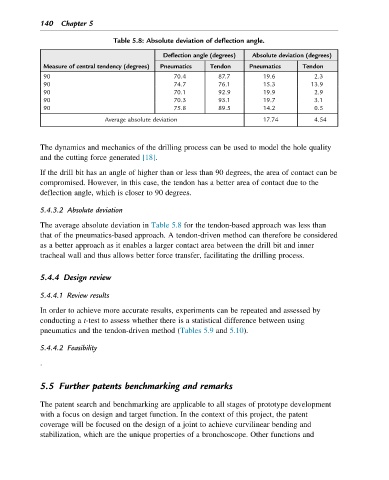
Table 5.8: Absolute deviation of deflection angle.
Deflection angle (degrees) Absolute deviation (degrees)
Measure of central tendency (degrees) Pneumatics Tendon Pneumatics Tendon
90 70.4 87.7 19.6 2.3
90 74.7 76.1 15.3 13.9
90 70.1 92.9 19.9 2.9
90 70.3 93.1 19.7 3.1
90 75.8 89.5 14.2 0.5
Average absolute deviation 17.74 4.54
The dynamics and mechanics of the drilling process can be used to model the hole quality
and the cutting force generated [18].
If the drill bit has an angle of higher than or less than 90 degrees, the area of contact can be
compromised. However, in this case, the tendon has a better area of contact due to the
deflection angle, which is closer to 90 degrees.
5.4.3.2 Absolute deviation
The average absolute deviation in Table 5.8 for the tendon-based approach was less than
that of the pneumatics-based approach. A tendon-driven method can therefore be considered
as a better approach as it enables a larger contact area between the drill bit and inner
tracheal wall and thus allows better force transfer, facilitating the drilling process.
5.4.4 Design review
5.4.4.1 Review results
In order to achieve more accurate results, experiments can be repeated and assessed by
conducting a t-test to assess whether there is a statistical difference between using
pneumatics and the tendon-driven method (Tables 5.9 and 5.10).
5.4.4.2 Feasibility
.
5.5 Further patents benchmarking and remarks
The patent search and benchmarking are applicable to all stages of prototype development
with a focus on design and target function. In the context of this project, the patent
coverage will be focused on the design of a joint to achieve curvilinear bending and
stabilization, which are the unique properties of a bronchoscope. Other functions and