Page 21 - Flexible Robotics in Medicine
P. 21
Slender snake-like endoscopic robots in surgery 3
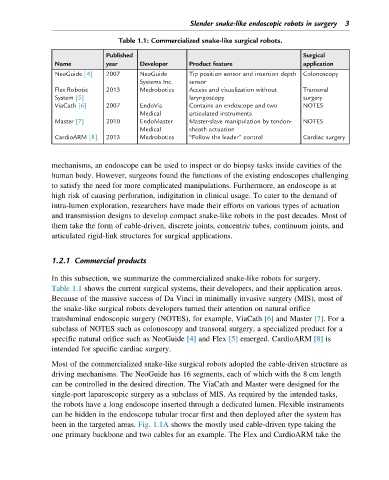
Table 1.1: Commercialized snake-like surgical robots.
Published Surgical
Name year Developer Product feature application
NeoGuide [4] 2007 NeoGuide Tip position sensor and insertion depth Colonoscopy
Systems Inc. sensor
Flex Robotic 2013 Medrobotics Access and visualization without Transoral
System [5] laryngoscopy surgery
ViaCath [6] 2007 EndoVia Contains an endoscope and two NOTES
Medical articulated instruments
Master [7] 2010 EndoMaster Master-slave manipulation by tendon- NOTES
Medical sheath actuation
CardioARM [8] 2013 Medrobotics “Follow the leader” control Cardiac surgery
mechanisms, an endoscope can be used to inspect or do biopsy tasks inside cavities of the
human body. However, surgeons found the functions of the existing endoscopes challenging
to satisfy the need for more complicated manipulations. Furthermore, an endoscope is at
high risk of causing perforation, indigitation in clinical usage. To cater to the demand of
intra-lumen exploration, researchers have made their efforts on various types of actuation
and transmission designs to develop compact snake-like robots in the past decades. Most of
them take the form of cable-driven, discrete joints, concentric tubes, continuum joints, and
articulated rigid-link structures for surgical applications.
1.2.1 Commercial products
In this subsection, we summarize the commercialized snake-like robots for surgery.
Table 1.1 shows the current surgical systems, their developers, and their application areas.
Because of the massive success of Da Vinci in minimally invasive surgery (MIS), most of
the snake-like surgical robots developers turned their attention on natural orifice
transluminal endoscopic surgery (NOTES), for example, ViaCath [6] and Master [7]. For a
subclass of NOTES such as colonoscopy and transoral surgery, a specialized product for a
specific natural orifice such as NeoGuide [4] and Flex [5] emerged. CardioARM [8] is
intended for specific cardiac surgery.
Most of the commercialized snake-like surgical robots adopted the cable-driven structure as
driving mechanisms. The NeoGuide has 16 segments, each of which with the 8 cm length
can be controlled in the desired direction. The ViaCath and Master were designed for the
single-port laparoscopic surgery as a subclass of MIS. As required by the intended tasks,
the robots have a long endoscope inserted through a dedicated lumen. Flexible instruments
can be hidden in the endoscope tubular trocar first and then deployed after the system has
been in the targeted areas. Fig. 1.1A shows the mostly used cable-driven type taking the
one primary backbone and two cables for an example. The Flex and CardioARM take the