Page 23 - Flexible Robotics in Medicine
P. 23
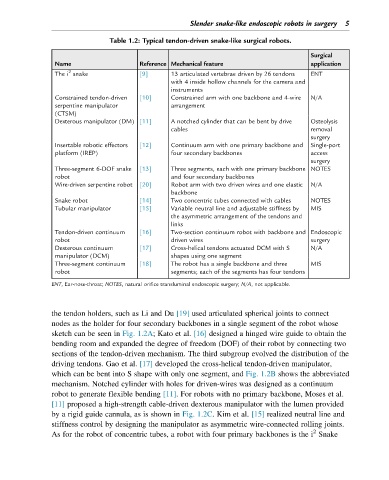
Slender snake-like endoscopic robots in surgery 5
Table 1.2: Typical tendon-driven snake-like surgical robots.
Surgical
Name Reference Mechanical feature application
2
The i snake [9] 13 articulated vertebrae driven by 26 tendons ENT
with 4 inside hollow channels for the camera and
instruments
Constrained tendon-driven [10] Constrained arm with one backbone and 4-wire N/A
serpentine manipulator arrangement
(CTSM)
Dexterous manipulator (DM) [11] A notched cylinder that can be bent by drive Osteolysis
cables removal
surgery
Insertable robotic effectors [12] Continuum arm with one primary backbone and Single-port
platform (IREP) four secondary backbones access
surgery
Three-segment 6-DOF snake [13] Three segments, each with one primary backbone NOTES
robot and four secondary backbones
Wire-driven serpentine robot [20] Robot arm with two driven wires and one elastic N/A
backbone
Snake robot [14] Two concentric tubes connected with cables NOTES
Tubular manipulator [15] Variable neutral line and adjustable stiffness by MIS
the asymmetric arrangement of the tendons and
links
Tendon-driven continuum [16] Two-section continuum robot with backbone and Endoscopic
robot driven wires surgery
Dexterous continuum [17] Cross-helical tendons actuated DCM with S N/A
manipulator (DCM) shapes using one segment
Three-segment continuum [18] The robot has a single backbone and three MIS
robot segments; each of the segments has four tendons
ENT, Ear-nose-throat; NOTES, natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery; N/A, not applicable.
the tendon holders, such as Li and Du [19] used articulated spherical joints to connect
nodes as the holder for four secondary backbones in a single segment of the robot whose
sketch can be seen in Fig. 1.2A; Kato et al. [16] designed a hinged wire guide to obtain the
bending room and expanded the degree of freedom (DOF) of their robot by connecting two
sections of the tendon-driven mechanism. The third subgroup evolved the distribution of the
driving tendons. Gao et al. [17] developed the cross-helical tendon-driven manipulator,
which can be bent into S shape with only one segment, and Fig. 1.2B shows the abbreviated
mechanism. Notched cylinder with holes for driven-wires was designed as a continuum
robot to generate flexible bending [11]. For robots with no primary backbone, Moses et al.
[11] proposed a high-strength cable-driven dexterous manipulator with the lumen provided
by a rigid guide cannula, as is shown in Fig. 1.2C. Kim et al. [15] realized neutral line and
stiffness control by designing the manipulator as asymmetric wire-connected rolling joints.
2
As for the robot of concentric tubes, a robot with four primary backbones is the i Snake