Page 333 - Flexible Robotics in Medicine
P. 333
Design evolution of a flexible robotic bending end-effector for transluminal explorations 323
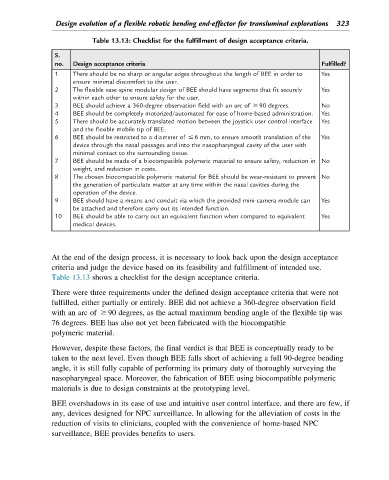
Table 13.13: Checklist for the fulfillment of design acceptance criteria.
S.
no. Design acceptance criteria Fulfilled?
1 There should be no sharp or angular edges throughout the length of BEE in order to Yes
ensure minimal discomfort to the user.
2 The flexible vase-spine modular design of BEE should have segments that fit securely Yes
within each other to ensure safety for the user.
3 BEE should achieve a 360-degree observation field with an arc of $ 90 degrees. No
4 BEE should be completely motorized/automated for ease of home-based administration. Yes
5 There should be accurately translated motion between the joystick user control interface Yes
and the flexible mobile tip of BEE.
6 BEE should be restricted to a diameter of # 6 mm, to ensure smooth translation of the Yes
device through the nasal passages and into the nasopharyngeal cavity of the user with
minimal contact to the surrounding tissue.
7 BEE should be made of a biocompatible polymeric material to ensure safety, reduction in No
weight, and reduction in costs.
8 The chosen biocompatible polymeric material for BEE should be wear-resistant to prevent No
the generation of particulate matter at any time within the nasal cavities during the
operation of the device.
9 BEE should have a means and conduit via which the provided mini-camera module can Yes
be attached and therefore carry out its intended function.
10 BEE should be able to carry out an equivalent function when compared to equivalent Yes
medical devices.
At the end of the design process, it is necessary to look back upon the design acceptance
criteria and judge the device based on its feasibility and fulfillment of intended use.
Table 13.13 shows a checklist for the design acceptance criteria.
There were three requirements under the defined design acceptance criteria that were not
fulfilled, either partially or entirely. BEE did not achieve a 360-degree observation field
with an arc of $ 90 degrees, as the actual maximum bending angle of the flexible tip was
76 degrees. BEE has also not yet been fabricated with the biocompatible
polymeric material.
However, despite these factors, the final verdict is that BEE is conceptually ready to be
taken to the next level. Even though BEE falls short of achieving a full 90-degree bending
angle, it is still fully capable of performing its primary duty of thoroughly surveying the
nasopharyngeal space. Moreover, the fabrication of BEE using biocompatible polymeric
materials is due to design constraints at the prototyping level.
BEE overshadows in its ease of use and intuitive user control interface, and there are few, if
any, devices designed for NPC surveillance. In allowing for the alleviation of costs in the
reduction of visits to clinicians, coupled with the convenience of home-based NPC
surveillance, BEE provides benefits to users.