Page 74 - Flexible Robotics in Medicine
P. 74
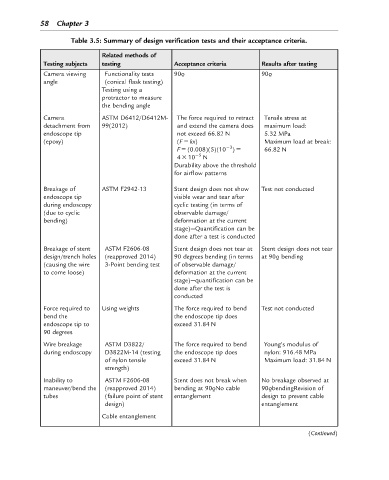
58 Chapter 3
Table 3.5: Summary of design verification tests and their acceptance criteria.
Related methods of
Testing subjects testing Acceptance criteria Results after testing
Camera viewing Functionality tests 90o 90o
% %
angle (conical flask testing)
Testing using a
protractor to measure
the bending angle
Camera ASTM D6412/D6412M- The force required to retract Tensile stress at
detachment from 99(2012) and extend the camera does maximum load:
endoscope tip not exceed 66.82 N 5.32 MPa
(epoxy) (F 5 kx) Maximum load at break:
23
F 5 (0.008)(5)(10 ) 5 66.82 N
4 3 10 25 N
Durability above the threshold
for airflow patterns
Breakage of ASTM F2942-13 Stent design does not show Test not conducted
endoscope tip visible wear and tear after
during endoscopy cyclic testing (in terms of
(due to cyclic observable damage/
bending) deformation at the current
stage)—Quantification can be
done after a test is conducted
Breakage of stent ASTM F2606-08 Stent design does not tear at Stent design does not tear
design/trench holes (reapproved 2014) 90 degrees bending (in terms at 90o bending
%
(causing the wire 3-Point bending test of observable damage/
to come loose) deformation at the current
stage)—quantification can be
done after the test is
conducted
Force required to Using weights The force required to bend Test not conducted
bend the the endoscope tip does
endoscope tip to exceed 31.84 N
90 degrees
Wire breakage ASTM D3822/ The force required to bend Young’s modulus of
during endoscopy D3822M-14 (testing the endoscope tip does nylon: 916.48 MPa
of nylon tensile exceed 31.84 N Maximum load: 31.84 N
strength)
Inability to ASTM F2606-08 Stent does not break when No breakage observed at
maneuver/bend the (reapproved 2014) bending at 90oNo cable 90obendingRevision of
% %
tubes (failure point of stent entanglement design to prevent cable
design) entanglement
Cable entanglement
(Continued)