Page 172 - Fluid Catalytic Cracking Handbook
P. 172
Unit Monitoring and Control 145
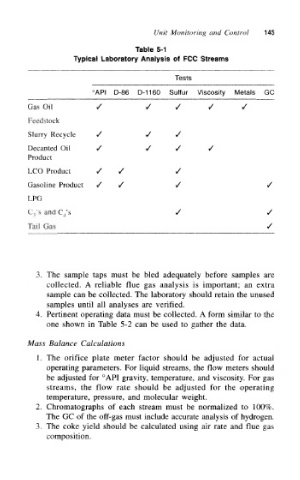
Table 5-1
Typical Laboratory Analysis of FCC Streams
Tests
°API D-86 D-1160 Sulfur Viscosity Metals GC
Gas Oil / / / / /
Feedstock
Slurry Recycle / / /
Decanted Oil / / / /
Product
LCO Product / / /
Gasoline Product / / / /
LPG
C.,\s and C 4's / /
Tail Gas /
3. The sample taps must be bled adequately before samples are
collected. A reliable flue gas analysis is important; an extra
sample can be collected. The laboratory should retain the unused
samples until all analyses are verified.
4. Pertinent operating data must be collected. A form similar to the
one shown in Table 5-2 can be used to gather the data.
Mass Balance Calculations
1. The orifice plate meter factor should be adjusted for actual
operating parameters. For liquid streams, the flow meters should
be adjusted for °API gravity, temperature, and viscosity. For gas
streams, the flow rate should be adjusted for the operating
temperature, pressure, and molecular weight.
2. Chromatographs of each stream must be normalized to 100%.
The GC of the off-gas must include accurate analysis of hydrogen,
3. The coke yield should be calculated using air rate and flue gas
composition.