Page 138 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 138
116 PUMPS, EJECTORS, BLOWERS, AND COMPRESSORS
& Sources for air/gas can be release of dissolved gas,
formation of slugs by entrained gas or through va-
porization of the liquid.
& Vaporization. Vaporization in the suction line can
also cause vapor lock. If the vapor formed is 10% or
more, vapor lock can occur.
➢ Vapor formation can be avoided by increasing
pressure through increase in level in the supply
tank, reducing frictional losses in suction line
through use of larger pipe diameters and minimum
number of fittings, valves, and so on, decreasing
liquid temperature by cooling or using a pump
with a lower NPSH R .
. Explain how pump capacity reduces if cavitation is
occurring.
& The formation of bubbles causes a volume increase,
decreasing the space available in the pump casing for
the liquid and thus diminishes pumping capacity. For
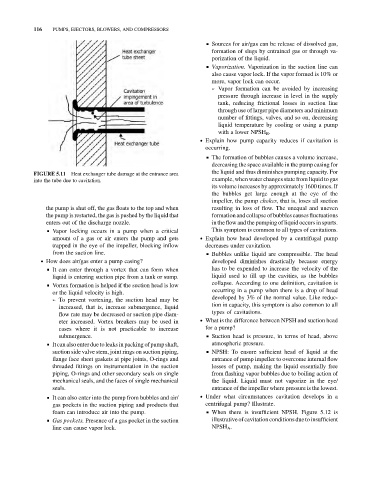
FIGURE 5.11 Heat exchanger tube damage at the entrance area
into the tube due to cavitation. example, when water changes state from liquid to gas
its volume increases by approximately 1600 times. If
the bubbles get large enough at the eye of the
impeller, the pump chokes, that is, loses all suction
the pump is shut off, the gas floats to the top and when resulting in loss of flow. The unequal and uneven
the pump is restarted, the gas is pushed by the liquid that formation and collapse of bubbles causes fluctuations
enters out of the discharge nozzle. in the flow and the pumping of liquid occurs in spurts.
& Vapor locking occurs in a pump when a critical This symptom is common to all types of cavitations.
amount of a gas or air enters the pump and gets . Explain how head developed by a centrifugal pump
trapped in the eye of the impeller, blocking inflow decreases under cavitation.
from the suction line. & Bubbles unlike liquid are compressible. The head
. How does air/gas enter a pump casing? developed diminishes drastically because energy
& It can enter through a vortex that can form when has to be expended to increase the velocity of the
liquid is entering suction pipe from a tank or sump. liquid used to fill up the cavities, as the bubbles
collapse. According to one definition, cavitation is
& Vortex formation is helped if the suction head is low
occurring in a pump when there is a drop of head
or the liquid velocity is high.
developed by 3% of the normal value. Like reduc-
➢ To prevent vortexing, the suction head may be
tion in capacity, this symptom is also common to all
increased, that is, increase submergence, liquid
types of cavitations.
flow rate may be decreased or suction pipe diam-
eter increased. Vortex breakers may be used in . What is the difference between NPSH and suction head
cases where it is not practicable to increase for a pump?
submergence. & Suction head is pressure, in terms of head, above
& It can also enter due to leaks in packing of pump shaft, atmospheric pressure.
suction side valve stem, joint rings on suction piping, & NPSH: To ensure sufficient head of liquid at the
flange face sheet gaskets at pipe joints, O-rings and entrance of pump impeller to overcome internal flow
threaded fittings on instrumentation in the suction losses of pump, making the liquid essentially free
piping, O-rings and other secondary seals on single from flashing vapor bubbles due to boiling action of
mechanical seals, and the faces of single mechanical the liquid. Liquid must not vaporize in the eye/
seals. entrance of the impeller where pressure is the lowest.
& It can also enter into the pump from bubbles and air/ . Under what circumstances cavitation develops in a
gas pockets in the suction piping and products that centrifugal pump? Illustrate.
foam can introduce air into the pump. & When there is insufficient NPSH. Figure 5.12 is
& Gas pockets. Presence of a gas pocket in the suction illustrativeof cavitation conditions due to insufficient
line can cause vapor lock. NPSH A .