Page 177 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 177
FANS, BLOWERS, AND COMPRESSORS 155
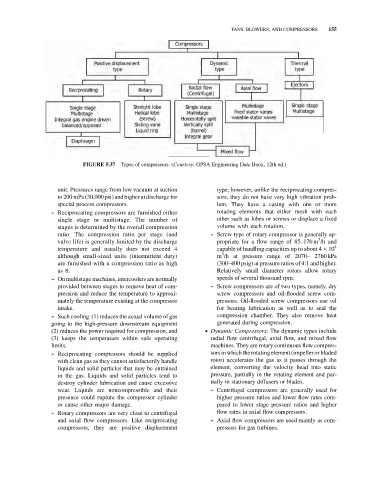
FIGURE 5.37 Types of compressors. (Courtesy: GPSA Engineering Data Book, 12th ed.)
unit. Pressures range from low vacuum at suction type; however, unlike the reciprocating compres-
to 200 mPa(30,000 psi) and higher at discharge for sors, they do not have very high vibration prob-
special process compressors. lem. They have a casing with one or more
➢ Reciprocating compressors are furnished either rotating elements that either mesh with each
single stage or multistage. The number of other such as lobes or screws or displace a fixed
stages is determined by the overall compression volume with each rotation.
ratio. The compression ratio per stage (and ➢ Screw type of rotary compressor is generally ap-
3
valve life) is generally limited by the discharge propriate for a flow range of 85–170 m /h and
temperature and usually does not exceed 4 capable of handling capacities up to about 4 10 4
3
although small-sized units (intermittent duty) m /h at pressure range of 2070– 2760 kPa
are furnished with a compression ratio as high (300–400 psig) at pressure ratios of 4:1 and higher.
as 8. Relatively small diameter rotors allow rotary
➢ On multistage machines, intercoolers are normally speeds of several thousand rpm.
provided between stages to remove heat of com- ➢ Screw compressors are of two types, namely, dry
pression and reduce the temperature to approxi- screw compressors and oil-flooded screw com-
mately the temperature existing at the compressor pressors. Oil-flooded screw compressors use oil
intake. for bearing lubrication as well as to seal the
➢ Such cooling (1) reduces the actual volume of gas compression chamber. They also remove heat
going to the high-pressure downstream equipment generated during compression.
(2) reduces the power required for compression, and & Dynamic Compressors: The dynamic types include
(3) keeps the temperature within safe operating radial flow centrifugal, axial flow, and mixed flow
limits. machines. They are rotary continuous flow compres-
➢ Reciprocating compressors should be supplied sors in which the rotating element (impeller or bladed
with clean gas as they cannot satisfactorily handle rotor) accelerates the gas as it passes through the
liquids and solid particles that may be entrained element, converting the velocity head into static
in the gas. Liquids and solid particles tend to pressure, partially in the rotating element and par-
destroy cylinder lubrication and cause excessive tially in stationary diffusers or blades.
wear. Liquids are noncompressible and their ➢ Centrifugal compressors are generally used for
presence could rupture the compressor cylinder higher pressure ratios and lower flow rates com-
or cause other major damage. pared to lower stage pressure ratios and higher
➢ Rotary compressors are very close to centrifugal flow rates in axial flow compressors.
and axial flow compressors. Like reciprocating ➢ Axial flow compressors are used mainly as com-
compressors, they are positive displacement pressors for gas turbines.