Page 241 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 241
TWO-PHASE FLOW 219
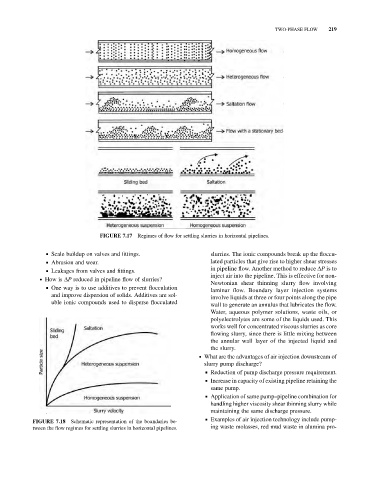
FIGURE 7.17 Regimes of flow for settling slurries in horizontal pipelines.
& Scale buildup on valves and fittings. slurries. The ionic compounds break up the floccu-
& Abrasion and wear. lated particles that give rise to higher shear stresses
in pipeline flow. Another method to reduce DP is to
& Leakages from valves and fittings.
inject air into the pipeline. This is effective for non-
. How is DP reduced in pipeline flow of slurries?
Newtonian shear thinning slurry flow involving
& One way is to use additives to prevent flocculation
laminar flow. Boundary layer injection systems
and improve dispersion of solids. Additives are sol-
involve liquids at three or four points along the pipe
uble ionic compounds used to disperse flocculated
wall to generate an annulus that lubricates the flow.
Water, aqueous polymer solutions, waste oils, or
polyelectrolytes are some of the liquids used. This
works well for concentrated viscous slurries as core
flowing slurry, since there is little mixing between
the annular wall layer of the injected liquid and
the slurry.
. What are the advantages of air injection downstream of
slurry pump discharge?
& Reduction of pump discharge pressure requirement.
& Increase in capacity of existing pipeline retaining the
same pump.
& Application of same pump–pipeline combination for
handling higher viscosity shear thinning slurry while
maintaining the same discharge pressure.
& Examples of air injection technology include pump-
FIGURE 7.18 Schematic representation of the boundaries be-
tween the flow regimes for settling slurries in horizontal pipelines. ing waste molasses, red mud waste in alumina pro-