Page 248 - Fluid mechanics, heat transfer, and mass transfer
P. 248
DIMENSIONLESS NUMBERS, TEMPERATURE MEASUREMENT, AND CONDUCTION HEAT TRANSFER
228
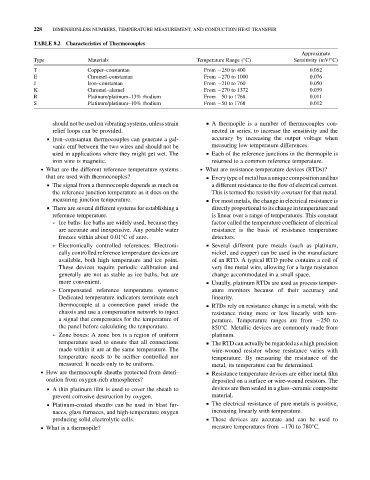
TABLE 8.2 Characteristics of Thermocouples
Approximate
Type Materials Temperature Range ( C) Sensitivity (mV/ C)
T Copper–constantan From 250 to 400 0.052
E Chromel–constantan From 270 to 1000 0.076
J Iron–constantan From 210 to 760 0.050
K Chromel–alumel From 270 to 1372 0.039
R Platinum/platinum–13% rhodium From 50 to 1768 0.011
S Platinum/platinum–10% rhodium From 50 to 1768 0.012
should not be used onvibrating systems, unless strain & A thermopile is a number of thermocouples con-
relief loops can be provided. nected in series, to increase the sensitivity and the
& Iron–constantan thermocouples can generate a gal- accuracy by increasing the output voltage when
vanic emf between the two wires and should not be measuring low temperature differences.
used in applications where they might get wet. The & Each of the reference junctions in the thermopile is
iron wire is magnetic. returned to a common reference temperature.
. What are the different reference temperature systems . What are resistance temperature devices (RTDs)?
that are used with thermocouples? & Every type of metal has a unique composition and has
& The signal from a thermocouple depends as much on a different resistance to the flow of electrical current.
the reference junction temperature as it does on the This is termed the resistivity constant for that metal.
measuring junction temperature. & For most metals, the change in electrical resistance is
& There are several different systems for establishing a directly proportional to its change in temperature and
reference temperature. is linear over a range of temperatures. This constant
➢ Ice baths: Ice baths are widely used, because they factor called the temperature coefficient of electrical
are accurate and inexpensive. Any potable water resistance is the basis of resistance temperature
freezes within about 0.01 C of zero. detectors.
➢ Electronically controlled references: Electroni- & Several different pure metals (such as platinum,
cally controlled reference temperature devices are nickel, and copper) can be used in the manufacture
available, both high temperature and ice point. of an RTD. A typical RTD probe contains a coil of
These devices require periodic calibration and very fine metal wire, allowing for a large resistance
generally are not as stable as ice baths, but are change accommodated in a small space.
more convenient. & Usually, platinum RTDs are used as process temper-
➢ Compensated reference temperature systems: ature monitors because of their accuracy and
Dedicated temperature indicators terminate each linearity.
thermocouple at a connection panel inside the & RTDs rely on resistance change in a metal, with the
chassis and use a compensation network to inject resistance rising more or less linearly with tem-
a signal that compensates for the temperature of perature. Temperature ranges are from 250 to
the panel before calculating the temperature. 850 C. Metallic devices are commonly made from
➢ Zone boxes: A zone box is a region of uniform platinum.
temperature used to ensure that all connections & The RTD can actually be regarded as a high precision
made within it are at the same temperature. The wire-wound resistor whose resistance varies with
temperature needs to be neither controlled nor temperature. By measuring the resistance of the
measured. It needs only to be uniform. metal, its temperature can be determined.
. How are thermocouple sheaths protected from deteri- & Resistance temperature devices are either metal film
oration from oxygen-rich atmospheres? deposited on a surface or wire-wound resistors. The
& A thin platinum film is used to cover the sheath to devices are then sealed in a glass–ceramic composite
prevent corrosive destruction by oxygen. material.
& Platinum-coated sheaths can be used in blast fur- & The electrical resistance of pure metals is positive,
naces, glass furnaces, and high-temperature oxygen increasing linearly with temperature.
producing solid electrolytic cells. & These devices are accurate and can be used to
. What is a thermopile? measure temperatures from 170 to 780 C.